突变型p53利用增强子在胰腺癌中提高免疫抑制趋化因子的表达并损害免疫检查点抑制剂,这一成果由麻省理工学院Phillip A. Sharp研究组经过不懈努力而取得。该研究于2025年6月30日发表于国际一流学术期刊《免疫学》杂志上。
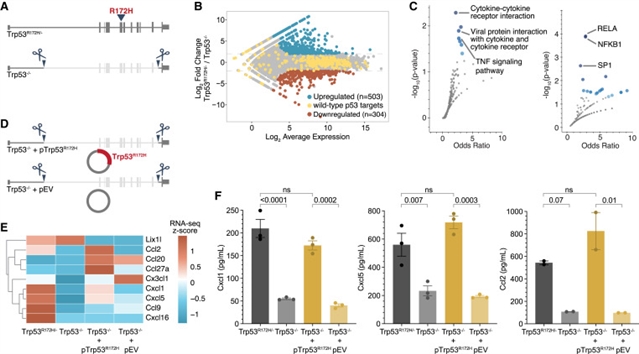
小组研究了p53错义突变是否具有潜在的功能获得性致癌作用及其对PDAC中癌细胞内在基因表达和肿瘤免疫微环境(TME)的影响。p53R172H通过调节一组不同的趋化因子,建立了免疫抑制TME,并损害了免疫检查点抑制剂(ICIs)的功效。其中,编码中性粒细胞化学引诱剂的Cxcl1的肿瘤特异性减少,促进T细胞浸润,降低肿瘤生长。机制上,p53R172H占据了Cxcl1的远端增强子并扩增了其表达。这些增强子负责Cxcl1的表达,并对其免疫抑制功能至关重要。核因子κB (NF-κB)是p53R172H占据这些增强子所需的关键辅因子。因此,肿瘤抑制转录因子中的一个常见突变适合增强子,从而刺激趋化因子的表达,并建立免疫抑制TME,从而降低PDAC中ICI的疗效。
据悉,胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)是一种高度侵袭性的癌症,其特征是激活KRAS突变和TP53改变。TP53错义突变失去了其野生型肿瘤抑制功能。
附:英文原文
Title: Mutant p53 exploits enhancers to elevate immunosuppressive chemokine expression and impair immune checkpoint inhibitors in pancreatic cancer
Author: Dig B. Mahat, Heena Kumra, Sarah A. Castro, Emily Metcalf, Kim Nguyen, Ryo Morisue, William W. Ho, Ivy Chen, Brandon Sullivan, Leon H. Yim, Arundeep Singh, Jiayu Fu, Sean K. Waterton, Yu-Chi Cheng, Enrico Moiso, Vikash P. Chauhan, Hernandez Moura Silva, Stefani Spranger, Rakesh K. Jain, Phillip A. Sharp
Issue&Volume: 2025-06-30
Abstract: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly aggressive cancer characterized by activating KRAS mutations and TP53 alterations. TP53 missense mutations lose their wild-type tumor-suppressor function. Here, we studied whether p53 missense mutations have potential gain-of-function oncogenic roles and their impact on cancer-cell-intrinsic gene expression and the tumor immune microenvironment (TME) in PDAC. p53R172H established an immunosuppressive TME and impaired the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) by regulating a distinct set of chemokines. Among these, tumor-specific reduction of Cxcl1, which encodes a chemoattractant for neutrophils, promoted T cell infiltration and decreased tumor growth. Mechanistically, p53R172H occupied the distal enhancers of Cxcl1 and amplified its expression. These enhancers were responsible for Cxcl1 expression and were essential for its immunosuppressive function. Nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) was a critical cofactor required for p53R172H occupancy at these enhancers. Thus, a common mutation in a tumor-suppressor transcription factor appropriates enhancers, thereby stimulating chemokine expression and establishing an immunosuppressive TME that diminishes ICI efficacy in PDAC.
DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2025.06.005
Source: https://www.cell.com/immunity/abstract/S1074-7613(25)00274-2
Immunity:《免疫》,创刊于1994年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:43.474
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/immunity/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/immunity/default.aspx
