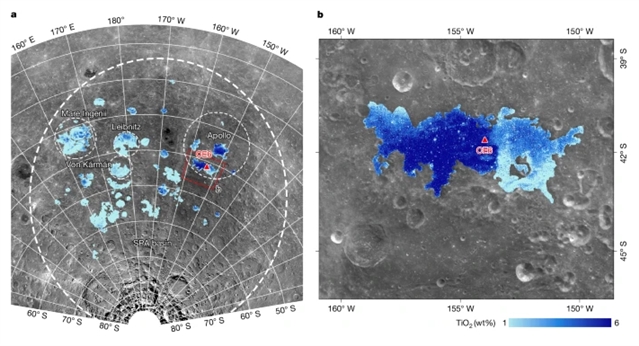
中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所吴福元团队近日研究了南极-艾特肯盆地玄武岩超贫地幔源。这一研究成果发表在2025年7月9日出版的《自然》杂志上。
月海玄武岩揭示了月球地幔的性质、月球成分的不对称性和早期月球岩浆海(LMO)。然而,月球背面广阔的南极-艾特肯盆地(SPA)下地幔的特征仍然是一个谜。
研究组分析了首次从SPA盆地返回的月球背面样品“嫦娥六号”(CE6)玄武岩碎片的岩石学和地球化学特征。这些28亿年前的CE6玄武岩与最进化的阿波罗12号钛铁矿玄武岩具有相似的主要元素组成。它们表现出极端的Sr-Nd耗竭,初始87Sr/86Sr比值为0.699237 ~ 0.699329,εNd(t)值(衡量钕同位素组成)为15.80 ~ 16.13。
这些特征表明地幔是由LMO结晶和/或熔体萃取导致的超贫地幔。前一种情况表明,近端和远端可能具有同位素相似的衰竭地幔端。后者可能与SPA撞击有关,表明增生后的大规模撞击可能引发下地幔的大规模熔体提取。无论如何,SPA盆地下的超贫地幔起源于LMO或后来的熔体提取,都为研究早期月红-幔分异提供了一个深入的观测窗口。
附:英文原文
Title: Ultra-depleted mantle source of basalts from the South Pole–Aitken basin
Author: Zhou, Qin, Yang, Wei, Chu, Zhuyin, Zhu, Honggang, Yang, Saihong, Zeng, Xingguo, Xue, Ding-Shuai, Jia, Li-Hui, Zhang, Guangliang, Zhang, Hongbo, Lin, Yanhao, Zhang, Huijuan, Tian, Heng-Ci, Peng, Peng, Zhang, Dan-Ping, Gu, Lixin, Li, Chunlai, Wu, Fu-Yuan
Issue&Volume: 2025-07-09
Abstract: Lunar mare basalts illuminate the nature of the Moon’s mantle, the lunar compositional asymmetry and the early lunar magma ocean (LMO)1,2,3. However, the characteristics of the mantle beneath the vast South Pole–Aitken (SPA) basin on the lunar farside remain a mystery. Here we present the petrology and geochemistry of basalt fragments from Chang’e-6 (CE6), the first returned lunar farside samples from the SPA basin4,5,6,7. These 2.8-billion-year-old CE6 basalts8 share similar major element compositions with the most evolved Apollo 12 ilmenite basalts. They exhibit extreme Sr–Nd depletion, with initial 87Sr/86Sr ratios of 0.699237 to 0.699329 and εNd(t) values (a measure of the neodymium isotopic composition) of 15.80 to 16.13. These characteristics indicate an ultra-depleted mantle, resulting from LMO crystallization and/or later depletion by melt extraction. The former scenario implies that the nearside and farside may possess an isotopically analogous depleted mantle endmember. The latter is probably related to the SPA impact, indicating that post-accretion massive impacts could have potentially triggered large-scale melt extraction of the underlying mantle. Either way, originating during the LMO or later melt extraction, the ultra-depleted mantle beneath the SPA basin offers a deep observational window into early lunar crust–mantle differentiation.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09131-7
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09131-7
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
