荷兰皇家艺术与科学学院Jop Kind小组在研究中取得进展。他们的最新研究报道了回顾性和多因子单细胞分析揭示了X失活过程中染色质的顺序重组。2025年7月10日出版的《自然—细胞生物学》发表了这项成果。
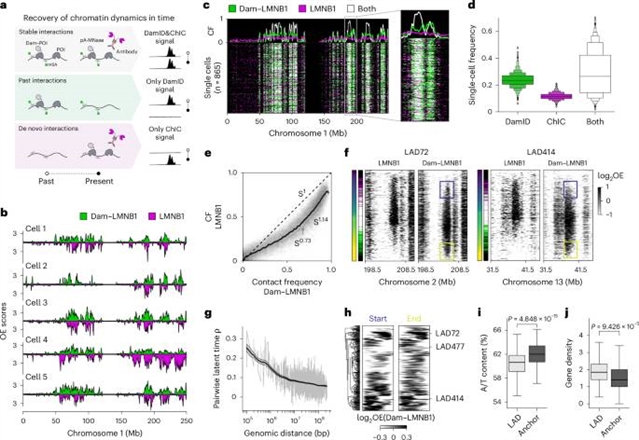
在这里,该课题组开发了Dam&ChIC,这是一种能够在单个细胞中进行回顾性和多因子染色质分析的方法。Dam&ChIC在带有m6A的活细胞中使用染色质标记来获得过去的染色质状态,再加上抗体介导的读数来捕获当前的染色质状态。多种因子组合的分析突出了其通用性和优越的分辨率。通过在细胞周期中跟踪层相关结构域遗传,该课题组人员发现Dam&ChIC提供了回溯性的单细胞染色质数据。当应用于随机X染色体失活时,Dam&ChIC解开了染色质重塑事件的时间顺序。在有丝分裂结束后,随着Xist的表达,在Polycomb扩散之前,失活的X染色体经历了广泛的基因组-膜分离。该研究组预计,Dam&ChIC将有助于揭示发育过程中细胞状态变化背后的基因调控事件的互联性和顺序。
研究人员表示,基因表达的调控是在染色质组织的多个水平上进行的。然而,基因调控是如何协调的仍未被探索。
附:英文原文
Title: Retrospective and multifactorial single-cell profiling reveals sequential chromatin reorganization during X inactivation
Author: Kefalopoulou, Samy, Rullens, Pim M. J., de Luca, Kim L., de Vries, Sandra S., Korthout, Tessy, van Oudenaarden, Alexander, Zeller, Peter, Kind, Jop
Issue&Volume: 2025-07-10
Abstract: The regulation of gene expression is governed at multiple levels of chromatin organization. However, how gene regulation is co-ordinated remains relatively unexplored. Here we develop Dam&ChIC, a method that enables retrospective and multifactorial chromatin profiling in single cells. Dam&ChIC employs chromatin labelling in living cells with m6A to acquire a past chromatin state, coupled with an antibody-mediated readout to capture the present chromatin state. Analyses of diverse factor combinations highlight its versatility and superior resolution. By tracking lamina-associated domain inheritance over the cell cycle, we showcase that Dam&ChIC provides retrospective single-cell chromatin data. When applied in random X chromosome inactivation, Dam&ChIC disentangles the temporal order of chromatin remodelling events. Upon mitotic exit and following Xist expression, the inactive X chromosome undergoes extensive genome–lamina detachment, preceding spreading of Polycomb. We anticipate that Dam&ChIC will be instrumental in unravelling the interconnectivity and order of gene-regulatory events underlying cell-state changes during development.
DOI: 10.1038/s41556-025-01687-w
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41556-025-01687-w
Nature Cell Biology:《自然—细胞生物学》,创刊于1999年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:28.213
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/ncb/
投稿链接:https://mts-ncb.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
