近日,英国牛津大学教授Dadson, Simon J.团队探明了气候变暖加剧了全球干旱的严重性。这一研究成果于2025年6月4日发表在《自然》杂志上。
干旱是影响全球环境、经济和人口的最常见和最复杂的自然灾害之一。然而,全球干旱趋势存在重大不确定性,对关键驱动因素大气蒸发需求(AED)在多大程度上影响干旱的幅度、频率、持续时间和面积范围的最新演变的理解有限。
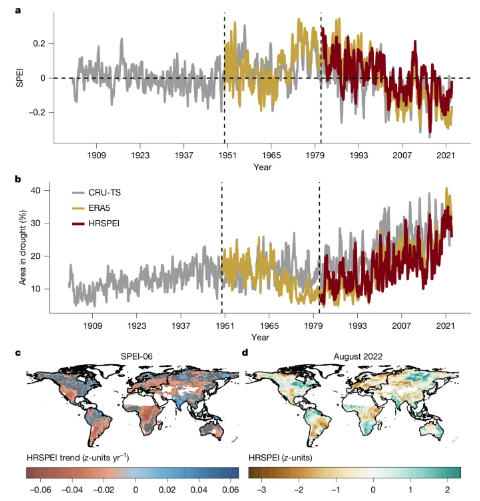
通过开发1901年至2022年的高分辨率全球干旱数据集,研究组发现全球干旱严重程度呈上升趋势。研究结果表明,AED使全球干旱严重程度平均增加了40%。不仅典型的干旱地区变得更干燥,潮湿地区也出现了干燥趋势。在过去的5 在2018年至2022年期间,干旱地区与1981年至2017年相比平均扩大了74%,其中AED占58%。
2022年是破纪录的一年,全球30%的陆地面积受到中度和极端干旱的影响,其中42%是由于AED增加造成的。该研究结果表明,AED在推动严重干旱方面发挥着越来越重要的作用,在未来的变暖情景下,这一趋势可能会持续下去。
附:英文原文
Title: Warming accelerates global drought severity
Author: Gebrechorkos, Solomon H., Sheffield, Justin, Vicente-Serrano, Sergio M., Funk, Chris, Miralles, Diego G., Peng, Jian, Dyer, Ellen, Talib, Joshua, Beck, Hylke E., Singer, Michael B., Dadson, Simon J.
Issue&Volume: 2025-06-04
Abstract: Drought is one of the most common and complex natural hazards affecting the environment, economies and populations globally1,2,3,4. However, there are significant uncertainties in global drought trends4,5,6, and a limited understanding of the extent to which a key driver, atmospheric evaporative demand (AED), impacts the recent evolution of the magnitude, frequency, duration and areal extent of droughts. Here, by developing an ensemble of high-resolution global drought datasets for 1901–2022, we find an increasing trend in drought severity worldwide. Our findings suggest that AED has increased drought severity by an average of 40% globally. Not only are typically dry regions becoming drier but also wet areas are experiencing drying trends. During the past 5years (2018–2022), the areas in drought have expanded by 74% on average compared with 1981–2017, with AED contributing to 58% of this increase. The year 2022 was record-breaking, with 30% of the global land area affected by moderate and extreme droughts, 42% of which was attributed to increased AED. Our findings indicate that AED has an increasingly important role in driving severe droughts and that this tendency will likely continue under future warming scenarios.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09047-2
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09047-2
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
