美国QuEra计算公司Alexei Bylinskii团队研究了(2 + 1)D 里德伯量子模拟器上弦断的观察。2025年6月4日出版的《自然》杂志发表了这项成果。
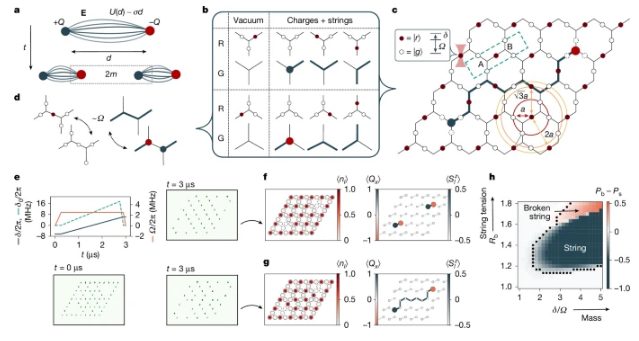
晶格规范理论(LGT)描述了凝聚态和粒子物理学中的一系列现象。一个突出的例子是约束,它负责将夸克束缚在强子(如质子或中子)内部。当夸克-反夸克对分离时,连接它们的胶子场串中存储的能量随着它们的距离线性增长,直到有足够的能量从真空中产生新的对并打破串。尽管这些现象在LGT中无处不在,但模拟由此产生的动力学是一项具有挑战性的任务。
研究组报告了使用基于中性原子阵列的可编程量子模拟器对合成量子物质中的弦断裂的观察。结果证明,当原子被放置在Kagome几何上时,可以有效地实现具有动态物质的(2+1)维LGT,其中局部U(1)对称性来自里德伯阻塞。长程里德伯相互作用自然会产生一对电荷的线性限制势,使人们能够调整它们的质量和弦张力。
研究组通过在存在缺陷的情况下绝热制备原子阵列的基态,区分由波动弦或断裂弦配置主导的受限相中的区域,实验性地探测平衡中的弦断裂。最后,通过利用对原子失谐的局部控制,研究组淬灭了弦态,并观察到弦断裂动力学表现出多体共振现象。该工作为使用可编程量子模拟器探索高能物理现象提供了机会。
附:英文原文
Title: Observation of string breaking on a (2 + 1)D Rydberg quantum simulator
Author: Gonzlez-Cuadra, Daniel, Hamdan, Majd, Zache, Torsten V., Braverman, Boris, Kornjaa, Milan, Lukin, Alexander, Cant, Sergio H., Liu, Fangli, Wang, Sheng-Tao, Keesling, Alexander, Lukin, Mikhail D., Zoller, Peter, Bylinskii, Alexei
Issue&Volume: 2025-06-04
Abstract: Lattice gauge theories (LGTs) describe a broad range of phenomena in condensed matter and particle physics. A prominent example is confinement, responsible for bounding quarks inside hadrons such as protons or neutrons1. When quark–antiquark pairs are separated, the energy stored in the string of gluon fields connecting them grows linearly with their distance, until there is enough energy to create new pairs from the vacuum and break the string. Although these phenomena are ubiquitous in LGTs, simulating the resulting dynamics is a challenging task2. Here we report the observation of string breaking in synthetic quantum matter using a programmable quantum simulator based on neutral atom arrays3,4,5. We show that a (2+1)-dimensional LGT with dynamical matter can be efficiently implemented when the atoms are placed on a Kagome geometry6, with a local U(1) symmetry emerging from the Rydberg blockade7. Long-range Rydberg interactions naturally give rise to a linear confining potential for a pair of charges, allowing us to tune both their masses and the string tension. We experimentally probe string breaking in equilibrium by adiabatically preparing the ground state of the atom array in the presence of defects, distinguishing regions within the confined phase dominated by fluctuating strings or by broken string configurations. Finally, by harnessing local control over the atomic detuning, we quench string states and observe string-breaking dynamics exhibiting a many-body resonance phenomenon. Our work provides opportunities for exploring phenomena in high-energy physics using programmable quantum simulators.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09051-6
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09051-6
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
