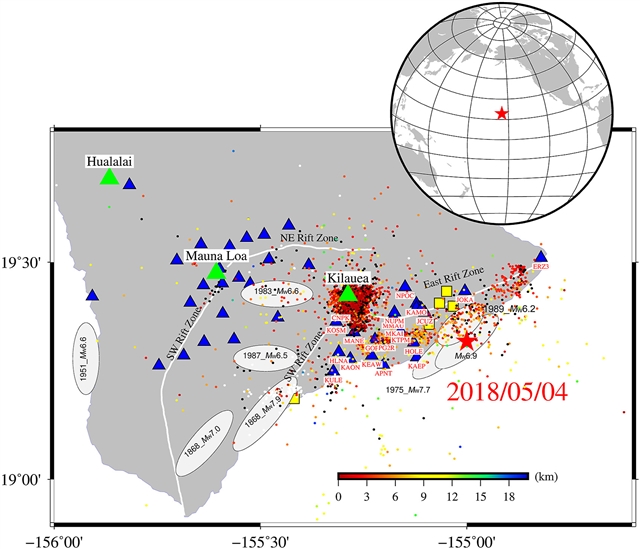
中国地震局地震预报研究所Lupeng Zhang团队研究了2018年夏威夷地震后Kīlauea火山活动的静态应力影响。这一研究成果于2025年6月3日发表在《大地测量与地球动力学》杂志上。
2018年5月4日,夏威夷发生的MW6.9逆冲断层地震发生在基拉韦厄盾状火山附近。研究组使用57天的连续全球定位系统(cGPS)数据和6天的半连续GPS数据来开发详细的同震滑动模型,并研究其对火山活动的影响。将这些数据与已发表的模型相结合,他们为2018年夏威夷地震重建了一个平面的、非常浅倾的几何模型。该结果显示,释放时刻约为4.05ⅹ1019 Nm(MW7.0),4.0 km深度处的峰值滑动约为2.4 m。
对比分析证实,同震模型对低倾角断层几何形状敏感,而对高倾角张开断层敏感。基于库仑破坏应力模型,研究组发现夏威夷事件对基拉韦厄的正应力大于对冒纳罗亚火山的正压力,主震对两座火山的岩浆房进行了减压,可能促进了东部裂谷带(ERZ)附近的岩浆通道和随后的喷发。主震还调整了震间蠕变、岩墙侵入和火山活动在事件发生前积累的静应力场。这项研究说明了地震序列和火山事件之间的物理相关性,为夏威夷基底断层沿线的孕震结构和应力扰动模式提供了见解。
附:英文原文
Title: Static stress implications for Kīlauea volcano activity after the 2018 Hawai'i earthquake
Author: Lupeng Zhang a
Issue&Volume: 2025/06/03
Abstract: The MW6.9 thrust-faulting earthquake in Hawai'i on May 4, 2018, occurred near the Kīlauea shield volcano. We use 57-day-long continuous Global Positioning System (cGPS) data and 6-day-long semi-continuous GPS data to develop a detailed coseismic slip model, and investigate its impact on volcanic activity. Combining these data with published models, we reconstruct a planar, very shallow dipping geometry model for the 2018 Hawai'i earthquake. Our results show the released moment is about 4.05ⅹ1019 Nm (MW7.0), with a peak slip of approximately 2.4 m at 4.0 km depth. Comparative analysis confirms that the coseismic model is sensitive to low-dip fault geometry rather than high-dip angle splay faults. Based on the Coulomb failure-stress model, we find the Hawai'i event exerts more positive stress on Kīlauea than on Mauna Loa, and the mainshock decompresses the magma chambers of both volcanoes, potentially facilitating magma pathways and subsequent eruptions near the east rift zone (ERZ). The mainshock also adjusts the static stress field accumulated by interseismic creep, dike intrusion, and volcanic activity before the event. This study illustrates the physical correlation between earthquake sequences and volcanic events, providing insights into the seismogenic structure and stress perturbation patterns along the Hawai'i basal décollement fault.
DOI: 10.1016/j.geog.2025.03.001
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S167498472500028X
Geodesy and Geodynamics:《大地测量与地球动力学》,创刊于2010年。隶属于爱思唯尔出版集团,最新IF:2.4
官方网址:https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/geodesy-and-geodynamics
投稿链接:https://www2.cloud.editorialmanager.com/geog/default2.aspx
