复旦大学上海医学院许彦晖小组在研究中取得进展。他们报道了人类Pol III转录起始的结构见解。这一研究成果发表在2025年6月4日出版的国际学术期刊《自然》上。
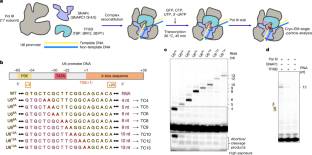
在这里,研究人员重组了7个人类Pol III转录复合物(TC4、TC5、TC6、TC8、TC10、TC12和TC13),它们停在U6启动子上,具有4-13个核苷酸的新生RNA。低温电镜结构捕获最初转录复合物(ITCs;TC4和TC5)和ECs(TC6-13)。与KMnO4足迹一起,数据揭示了广泛的模块化重排:转录泡从PIC扩展到TC5,随后是一般转录因子(GTF)解离和从TC5到TC6的突然泡崩溃,标志着ITC-EC过渡。在TC5中,SNAPc和TFIIIB仍然与启动子和Pol III结合,而RNA-DNA杂交体采用倾斜构象,模板DNA被TFIIIB亚基BRF2阻断。在ITC-EC转换过程中,杂交前向易位触发BRF2手指收缩、GTF释放和转录泡崩溃。然后,当GTF停留在上游时,Pol III逃离启动子,可能使重新启动成为可能。这些发现揭示了高需求小RNA的3型启动子的Pol III动力学和再启动机制的分子见解,以及最早记录的RNA聚合酶的起始-延伸转变。
研究人员表示,RNA聚合酶III (RNA polymerase III, Pol III)转录的高需求RNA分为三类经典启动子,包括1型(5S rRNA)、2型(tRNA)和3型(短非编码RNA,如U6、7SK和RNase H1)启动子。虽然已经确定了Pol III预起始络合物(PIC)和延伸络合物(EC)的结构,但从起始到延伸的转变机制尚不清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: Structural insights into human Pol III transcription initiation in action
Author: Wang, Qianmin, Ren, Yulei, Jin, Qianwei, Chen, Xizi, Xu, Yanhui
Issue&Volume: 2025-06-04
Abstract: RNA polymerase III (Pol III) transcribes highly demanded RNAs grouped into three types of classical promoters, including type 1 (5S rRNA), type 2 (tRNA) and type 3 (short non-coding RNAs, such as U6, 7SK and RNase H1) promoters1,2,3,4,5,6,7. While structures of the Pol III preinitiation complex (PIC)8,9,10,11 and elongation complex (EC)12,13,14,15,16 have been determined, the mechanism underlying the transition from initiation to elongation remains unclear. Here we reconstituted seven human Pol III transcribing complexes (TC4, TC5, TC6, TC8, TC10, TC12 and TC13) halted on U6 promoters with nascent RNAs of 4–13 nucleotides. Cryo-electron microscopy structures captured initially transcribing complexes (ITCs; TC4 and TC5) and ECs (TC6–13). Together with KMnO4 footprinting, the data reveal extensive modular rearrangements: the transcription bubble expands from PIC to TC5, followed by general transcription factor (GTF) dissociation and abrupt bubble collapse from TC5 to TC6, marking the ITC–EC transition. In TC5, SNAPc and TFIIIB remain bound to the promoter and Pol III, while the RNA–DNA hybrid adopts a tilted conformation with template DNA blocked by BRF2, a TFIIIB subunit. Hybrid forward translocation during ITC–EC transition triggers BRF2-finger retraction, GTF release and transcription-bubble collapse. Pol III then escapes the promoter while GTFs stay bound upstream, potentially enabling reinitiation. These findings reveal molecular insights into Pol III dynamics and reinitiation mechanisms on type 3 promoters of highly demanded small RNAs, with the earliest documented initiation–elongation transition for an RNA polymerase.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09093-w
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09093-w
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
