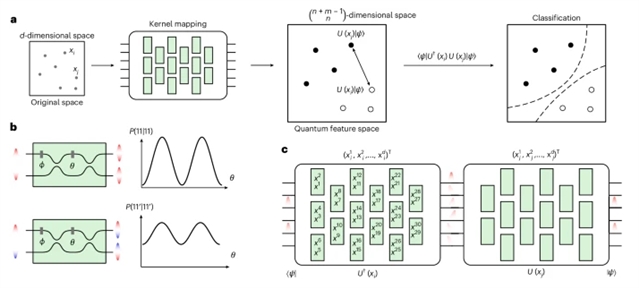
近日,奥地利维也纳量子科学与技术中心Philip Walther团队研究了光子处理器上基于核的实验量子增强机器学习。2025年6月2日出版的《自然—光子学》杂志发表了这一最新研究成果。
最近,机器学习在科学到日常生活的应用中产生了显著的影响。然而,复杂的任务通常需要消耗不可行的能量和计算能力。量子计算可能会降低这些要求,尽管目前尚不清楚当前技术是否可以实现增强。
研究组演示了一种在光子集成处理器上执行二进制分类任务的内核方法。他们证明,通过利用量子干涉,该协议优于高斯核和神经切线核等最先进的核方法,并通过提供单光子相干性进一步提高了精度。我们的方案不需要纠缠门,可以通过额外的模式和注入的光子来修改系统维度。这一结果使我们能够获得更高效的算法,并制定量子效应改进标准方法的任务。
附:英文原文
Title: Experimental quantum-enhanced kernel-based machine learning on a photonic processor
Author: Yin, Zhenghao, Agresti, Iris, de Felice, Giovanni, Brown, Douglas, Toumi, Alexis, Pentangelo, Ciro, Piacentini, Simone, Crespi, Andrea, Ceccarelli, Francesco, Osellame, Roberto, Coecke, Bob, Walther, Philip
Issue&Volume: 2025-06-02
Abstract: Recently, machine learning has had remarkable impact in scientific to everyday-life applications. However, complex tasks often require the consumption of unfeasible amounts of energy and computational power. Quantum computation may lower such requirements, although it is unclear whether enhancements are reachable with current technologies. Here we demonstrate a kernel method on a photonic integrated processor to perform a binary classification task. We show that our protocol outperforms state-of-the-art kernel methods such as gaussian and neural tangent kernels by exploiting quantum interference, and provides further improvements in accuracy by offering single-photon coherence. Our scheme does not require entangling gates and can modify the system dimension through additional modes and injected photons. This result gives access to more efficient algorithms and to formulating tasks where quantum effects improve standard methods.
DOI: 10.1038/s41566-025-01682-5
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-025-01682-5
