|
|
|
|
|
FMD 论文速览:5′-tiRNA-Gln通过与真核起始因子4A-I相互作用抑制翻译来抑制肝细胞癌进展 |
|
|
论文标题:5′-tiRNA-Gln inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by repressing translation through the interaction with eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-I
期刊: Frontiers of Medicine
作者:Chengdong Wu, Dekai Liu, Lufei Zhang, Jingjie Wang, Yuan Ding, Zhongquan Sun, Weilin Wang
发表时间:15 Jun 2023
DOI:10.1007/s11684-022-0966-6
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章
导 读
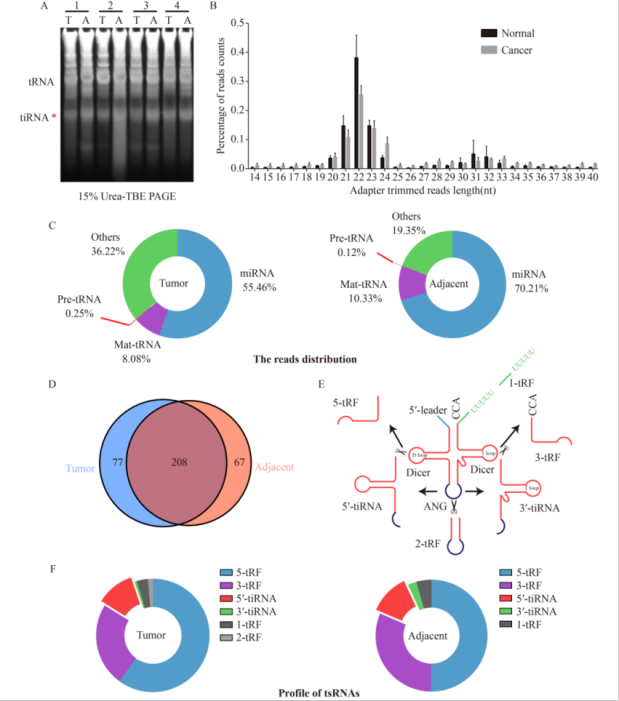
浙江大学癌症研究院王伟林团队在Frontiers of Medicine发表研究论文《5′-tiRNA-Gln通过与真核起始因子4A-I相互作用抑制翻译来抑制肝细胞癌进展》(5′-tiRNA-Gln inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by repressing translation through the interaction with eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-I)。本文运用多种实验技术,构建了肝癌患者tsRNA文库并分析差异表达的tsRNAs,发现5′-tiRNA-Gln在肝癌组织中显著下调,与肿瘤大小和转移密切相关。研究为肝癌预后评估和治疗提供了新的潜在靶点。
tRNA-derived small RNAs (tsRNAs) are novel non-coding RNAs that are involved in the occurrence and progression of diverse diseases. However, their exact presence and function in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain unclear. Here, differentially expressed tsRNAs in HCC were profiled. A novel tsRNA, tRNAGln-TTG derived 5′-tiRNA-Gln, is significantly downregulated, and its expression level is correlated with progression in patients. In HCC cells, 5′-tiRNA-Gln overexpression impaired the proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro and in vivo, while 5′-tiRNA-Gln knockdown yielded opposite results. 5′-tiRNA-Gln exerted its function by binding eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-I (EIF4A1), which unwinds complex RNA secondary structures during translation initiation, causing the partial inhibition of translation. The suppressed downregulated proteins include ARAF, MEK1/2 and STAT3, causing the impaired signaling pathway related to HCC progression. Furthermore, based on the construction of a mutant 5′-tiRNA-Gln, the sequence of forming intramolecular G-quadruplex structure is crucial for 5′-tiRNA-Gln to strongly bind EIF4A1 and repress translation. Clinically, 5′-tiRNA-Gln expression level is negatively correlated with ARAF, MEK1/2, and STAT3 in HCC tissues. Collectively, these findings reveal that 5′-tiRNA-Gln interacts with EIF4A1 to reduce related mRNA binding through the intramolecular G-quadruplex structure, and this process partially inhibits translation and HCC progression.
tRNA衍生的小RNA(tsRNAs)是一类新型的非编码RNA,参与多种疾病的发生和发展。然而,它们在肝细胞癌(HCC)中的具体存在情况和功能仍不清楚。本研究对HCC中差异表达的tsRNAs进行了分析。研究发现,一种由tRNAGln-TTG衍生的新型tsRNA——5′-tiRNA-Gln显著下调,其表达水平与患者的病情进展相关。在HCC细胞中,过表达5′-tiRNA-Gln在体外和体内均抑制了细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭能力,而敲低5′-tiRNA-Gln则产生相反的结果。5′-tiRNA-Gln通过与真核起始因子4A-I (EIF4A1)结合发挥作用,EIF4A1在翻译起始过程中解开复杂的RNA二级结构,从而部分抑制翻译。被抑制下调的蛋白质包括ARAF、MEK1/2和STAT3,这导致与HCC进展相关的信号通路受损。此外,通过构建突变型5′-tiRNA-Gln发现,形成分子内G-四链体结构的序列对于5′-tiRNA-Gln与EIF4A1的强结合和抑制翻译至关重要。临床上,HCC组织中5′-tiRNA-Gln的表达水平与ARAF、MEK1/2和STAT3呈负相关。综上所述,这些发现揭示了5′-tiRNA-Gln通过分子内G-四链体结构与EIF4A1相互作用,减少相关mRNA的结合,这一过程部分抑制了翻译,进而抑制了HCC的进展。
期刊介绍
Frontiers of Medicine专注于发表临床医学和基础医学领域的最新研究成果,旨在通过全球医疗专业人员之间的交流促进健康和医疗保健的发展。该刊采用严格的同行评审和编辑流程,确保发表的文章的科学准确性、新颖性和重要性。
原文信息
标题
5′-tiRNA-Gln inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by repressing translation through the interaction with eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-I
作者
Chengdong Wu, Dekai Liu, Lufei Zhang, Jingjie Wang, Yuan Ding, Zhongquan Sun, Weilin Wang
机构
Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310009, China; Key Laboratory of Precision Diagnosis and Treatment for Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Tumor of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou 310009, China; Research Center of Diagnosis and Treatment Technology for Hepatocellular Carcinoma of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou 310009, China; Clinical Medicine Innovation Center of Precision Diagnosis and Treatment for Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease of Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310009, China; Clinical Research Center of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou 310009, China; Cancer Center, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310009, China
通讯作者
Weilin Wang
引用这篇文章
Chengdong Wu, Dekai Liu, Lufei Zhang, Jingjie Wang, Yuan Ding, Zhongquan Sun, Weilin Wang. 5′-tiRNA-Gln inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by repressing translation through the interaction with eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-I. Front. Med., 2023, 17(3): 476–492 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-022-0966-6
https://journal.hep.com.cn/fmd/EN/10.1007/s11684-022-0966-6
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11684-022-0966-6
感谢作者对Frontiers of Medicine的信任和支持。

《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中12种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。