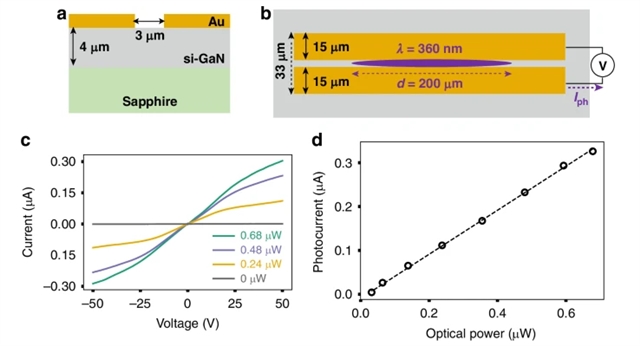
美国加州大学伯克利分校Feng Wang团队近日利用氮化镓光导发射体实现了片上太赫兹的高效产生和检测。2025年6月25日出版的《光:科学与应用》杂志发表了这项成果。
太赫兹产生的光导发射器有望实现光子的高效下转换,因为它不受曼利-罗关系的限制。然而,由于常用GaAs材料的半导体特性,现有的太赫兹光电导器件在效率方面面临限制。研究组证明了以高击穿电场为特征的大带隙半导体GaN有助于在共面带状线波导中高效产生太赫兹波。为了实现这一目标,他们通过实验和第一性原理计算研究了激子对GaN在静电场下电光响应的贡献,揭示了一个稳健的激子斯塔克位移。
利用这种电光效应,研究组开发了一种新型的紫外泵浦探针光谱,用于原位表征GaN光电导发射器产生的太赫兹电场强度。该研究结果表明,太赫兹功率在宽参数范围内与光激发功率和施加电场呈二次方关系。在该实验中,最高偏置场(116千伏/厘米)条件下,他们在0.03~1太赫兹带宽范围内实现了接近100%的光学-太赫兹转换效率。GaN基太赫兹产生器件的进一步优化可以实现更高的光到太赫兹转换效率。
附:英文原文
Title: Efficient on-chip terahertz generation and detection with GaN photoconductive emitters
Author: Uzundal, Can B., Feng, Qixin, Tang, Weichen, Hu, Chen, Sanborn, Collin, Yoon, Yoseob, Chen, Sudi, Ruan, Jiawei, Louie, Steven G., Wang, Feng
Issue&Volume: 2025-06-25
Abstract: Photoconductive emitters for terahertz generation hold promise for highly efficient down-conversion of optical photons because it is not constrained by the Manley-Rowe relation. Existing terahertz photoconductive devices, however, faces limits in efficiency due to the semiconductor properties of commonly used GaAs materials. Here, we demonstrate that large bandgap semiconductor GaN, characterized by its high breakdown electric field, facilitates the highly efficient generation of terahertz waves in a coplanar stripline waveguide. Towards this goal, we investigated the excitonic contribution to the electro-optic response of GaN under static electric field both through experiments and first-principles calculations, revealing a robust excitonic Stark shift. Using this electro-optic effect, we developed a novel ultraviolet pump-probe spectroscopy for in-situ characterization of the terahertz electric field strength generated by the GaN photoconductive emitter. Our findings show that terahertz power scales quadratically with optical excitation power and applied electric field over a broad parameter range. We achieved an optical-to-terahertz conversion efficiency approaching 100% within the 0.03–1THz bandwidth at the highest bias field (116kV/cm) in our experiment. Further optimization of GaN-based terahertz generation devices could achieve even greater optical-to-terahertz conversion efficiencies.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-01870-6
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-01870-6
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
