中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所魏勇团队研究了蒙德极小期附近古代极光记录的比较分析。相关论文于2025年6月23日发表在《中国科学:地球科学》杂志上。
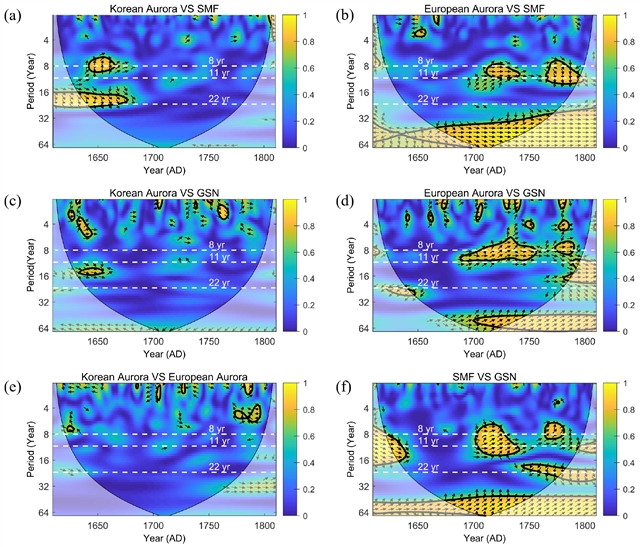
地球上的极光与太阳活动密切相关,为研究太阳活动的变化提供了一种有价值的方法,特别是在太阳活动数据稀缺的时期。研究组比较并分析了公元1610年至1810年间韩国和中纬度欧洲的极光记录。韩国和欧洲的极光记录都显示出极光活动与太阳变化的一致性,在不同时期具有明显的优势。
在公元1700年之前,韩国的极光观测比欧洲的极光更频繁,并且与太阳活动的代用物很好地吻合,使它们成为研究蒙德极小期太阳变化的特别主题。公元1700年以后,欧洲的极光记录比韩国的更为丰富,且与太阳活动相一致,有助于更好地了解蒙德极小期后的太阳变化和太阳活动的长期趋势。因此,韩国和欧洲的极光数据相互补充,增强了他们对历史太阳活动的理解。
附:英文原文
Title: Comparative analysis of ancient aurorae records near the Maunder Minimum
Author: Si CHEN, Yong WEI, Hong YUAN, Xin’an YUE, Fei HE, Limei YAN, Kai FAN, Yuqi WANG
Issue&Volume: 2025/06/23
Abstract: Auroras on Earth are closely linked to solar activity, offering a valuable way to investigate variations in solar activity, particularly for periods when solar activity data are scarce. This study compares and analyzes auroral records from Korea and mid-latitude Europe between 1610 and 1810 AD. Both Korean and European aurora records show consistency between auroral activity and solar variations, with distinct advantages in different periods. Before 1700 AD, Korean auroral observations were more frequent than European auroras and aligned well with solar activity proxies, making them particularly useful for studying solar variability during the Maunder Minimum. After 1700 AD, European auroral records became more abundant than Korean auroral records and consistent with solar activity, providing better insights into post-Maunder Minimum solar variations and long-term solar activity trends. Thus, Korean and European auroral data complement each other, enhancing our understanding of historical solar activity.
DOI: 10.1007/s11430-024-1600-6
Source: https://www.sciengine.com/SCES/doi/10.1007/s11430-024-1600-6
Science China Earth Sciences:《中国科学:地球科学》,创刊于1952年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:5.7
官方网址:https://www.sciengine.com/SCES/home
投稿链接:https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/sces
