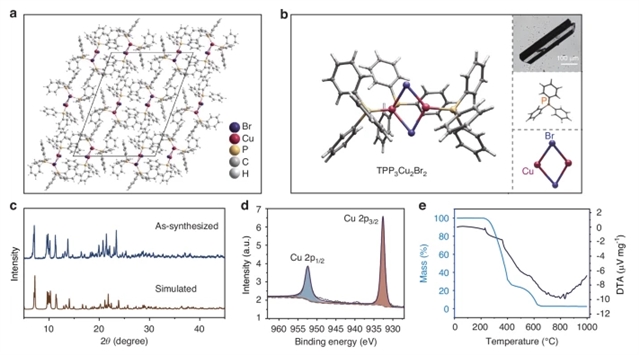
中国科学院福建物质结构研究所陈学元团队研究了基于混合卤化亚铜的发光寿命温度计,其具有出色的耐水性和巨大的热膨胀性。相关论文于2025年6月24日发表在《光:科学与应用》杂志上。
光学探针因其快速响应、高空间分辨率和远程非侵入性检测等吸引人的特性,在温度传感方面具有巨大的前景。然而,测温探头的探索受到其相对灵敏度(Sr)低或水中结构稳定性差的阻碍。研究组提出了基于TPP3Cu2Br2(TPP = 三苯基膦)的有机-无机金属卤化物的第一个例子,其同时在水中表现出优异的耐水性和灵敏的温度依赖性光致发光寿命。得益于TPP有机分子诱导的软晶格,随着温度的升高,实现了巨大的热膨胀和晶格畸变。
因此,TPP3Cu2Br2的自陷激子发光寿命可以从280K缩短到380K,缩短到初始值的1.9%,在未掺杂的金属卤化物基发光温度计中,Sr的含量最高,为12.82%K-1。值得注意的是,TPP3Cu2Br2表现出非凡的水稳定性,在水中浸泡15天后,发射强度几乎保持不变。此外,成功地在水环境中进行了高精度的基于发光寿命的热传感,证明其对水中的检测深度是惰性的,读出误差很小。这项工作为探索用于高灵敏度测温探头的新型金属卤化物提供了新的途径,使其适用于多种应用场景。
附:英文原文
Title: Luminescence lifetime thermometers based on hybrid cuprous halides with exceptional water resistance and giant thermal expansion
Author: Li, Chenliang, Wang, Luping, Tu, Datao, Shang, Xiaoying, Yang, Mingjie, Gong, Jiacheng, Wen, Fei, Xing, Yun, Xie, Zhi, Jiang, Jiaxin, Yu, Shaohua, Chen, Xueyuan
Issue&Volume: 2025-06-24
Abstract: Optical probes hold great promise for temperature sensing owing to their attractive properties including rapid response, high spatial resolution, and remote non-invasive detection. However, the exploration of thermometric probes is hindered by their low relative sensitivity (Sr) or poor structural stability in water. Herein, we propose the first example of organic-inorganic metal halides based on TPP3Cu2Br2 (TPP=triphenylphosphine) that simultaneously present excellent water resistance and sensitive temperature-dependent photoluminescence lifetime in water. Benefiting from the soft lattice induced by the organic molecule of TPP, giant thermal expansion and great lattice distortion were achieved with increasing temperature. As such, the self-trapped exciton luminescence lifetime of TPP3Cu2Br2 can be shortened to 1.9% of the initial value from 280 to 380K, resulting in the highest Sr of 12.82% K1 among the undoped metal halides based luminescent thermometers. Significantly, TPP3Cu2Br2 displayed extraordinary water stability with emission intensity remaining nearly unchanged after immersing in water for 15 days. Moreover, high-precision luminescence lifetime based thermal sensing in water environment was successfully conducted, which proved to be inert to the detection depth in water with a small read-out error. This work offers new routes in the exploration of novel metal halides for highly sensitive thermometric probes toward versatile application scenarios.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-01910-1
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-01910-1
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
