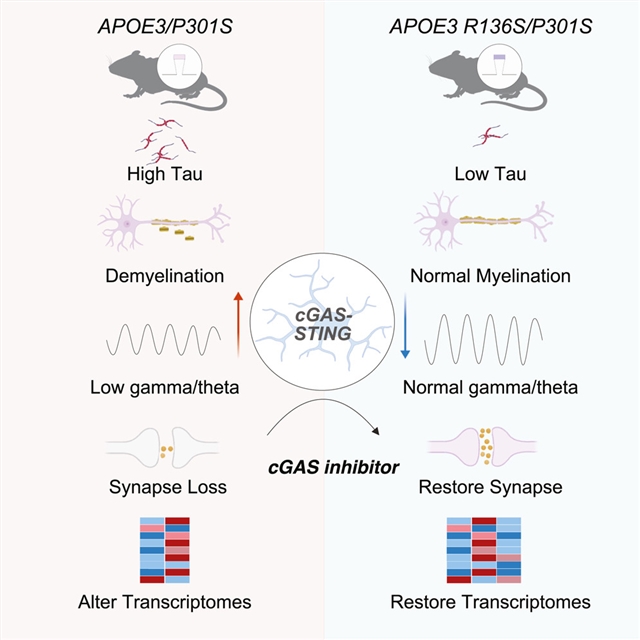
近日,美国威尔康奈尔医学院教授Li Gan及其课题组的研究认为APOE3基因的R136S突变通过抑制cGAS-STING-IFN通路赋予tau病理的恢复能力。相关论文发表在2025年6月23日出版的《免疫学》杂志上。
该研究组将小鼠Apoe替换为野生型人类APOE3或APOE3S/S。R136S突变降低tau负荷,防止tau诱导的突触丧失、髓磷脂丧失以及海马θ和γ功率的降低。此外,R136S突变降低了干扰素对小鼠和人小胶质细胞tau病理的反应,抑制了cGAS-STING通路的激活。用cGAS抑制剂治疗E3牛头病小鼠,可以防止tau诱导的突触丧失,并诱导类似于R136S突变的转录组改变。因此,抑制小胶质细胞cGAS-STING干扰素(IFN)通路在介导R136S对牛头病的保护作用中起着核心作用。
研究人员表示,APOE3 (E3S/S)基因的Christchurch突变(R136S)与tau负荷减弱和认知能力下降有关,尽管携带者存在致病性PSEN1突变和高淀粉样蛋白负荷。然而,使E3S/S突变减轻tau诱导的神经变性的分子机制尚不清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: The R136S mutation in the APOE3 gene confers resilience against tau pathology via inhibition of the cGAS-STING-IFN pathway
Author: Sarah Naguib, Chloe Lopez-Lee, Eileen Ruth Torres, Se-In Lee, Jingjie Zhu, Daphne Zhu, Pearly Ye, Kendra Norman, Mingrui Zhao, Man Ying Wong, Yohannes A. Ambaw, Rodrigo Muoz-Castaeda, Wei Wang, Tark Patel, Maitreyee Bhagwat, Rada Norinsky, Sue-Ann Mok, Tobias C. Walther, Robert V. Farese, Wenjie Luo, Subhash C. Sinha, Zhuhao Wu, Li Fan, Shiaoching Gong, Li Gan
Issue&Volume: 2025-06-23
Abstract: The Christchurch mutation (R136S) in the APOE3 (E3S/S) gene is associated with attenuated tau load and cognitive decline despite the presence of a causal PSEN1 mutation and high amyloid burden in the carrier. However, the molecular mechanisms enabling the E3S/S mutation to mitigate tau-induced neurodegeneration remain unclear. Here, we replaced mouse Apoe with wild-type human APOE3 or APOE3S/S on a tauopathy background. The R136S mutation decreased tau load and protected against tau-induced synaptic loss, myelin loss, and reduction in hippocampal theta and gamma power. Additionally, the R136S mutation reduced interferon responses to tau pathology in both mouse and human microglia, suppressing cGAS-STING pathway activation. Treating E3 tauopathy mice with a cGAS inhibitor protected against tau-induced synaptic loss and induced transcriptomic alterations similar to the R136S mutation across brain cell types. Thus, suppression of the microglial cGAS-STING-interferon (IFN) pathway plays a central role in mediating the protective effects of R136S against tauopathy.
DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2025.05.023
Source: https://www.cell.com/immunity/abstract/S1074-7613(25)00244-4
Immunity:《免疫》,创刊于1994年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:43.474
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/immunity/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/immunity/default.aspx
