英国圣安德鲁斯大学Wahl, Peter团队近日研究了相关流动铁磁体中紧急交换驱动的巨磁弹性耦合。这一研究成果于2025年6月17日发表在《自然—物理学》杂志上。
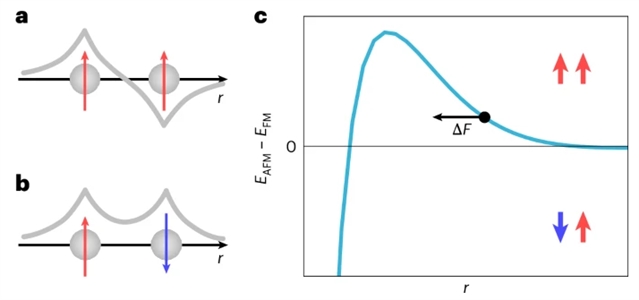
电子自由度和结构自由度之间的相互作用是凝聚态物理学中观察到的几个有趣现象的核心。在磁性材料中,磁相互作用与晶格自由度耦合,导致磁弹性耦合,这种耦合通常很小,只能在宏观样品中检测到。研究组证明了相关巡回铁磁体Sr4Ru3O10中的巨磁弹性耦合。他们建立了对表层磁性的有效控制,并利用它来探索磁性对其电子和结构性能的影响。
通过使用扫描隧道显微镜,研究组揭示了电子结构的微妙变化,这取决于表面和次表面层之间的铁磁或反铁磁排列。他们进一步确定了交换力对表层弛豫的影响,表层表现出巨大的磁致伸缩。该研究结果直接测量了交换相互作用和相关性对量子材料结构细节的影响,揭示了电子相关性如何导致强烈的电子-晶格耦合。
附:英文原文
Title: Emergent exchange-driven giant magnetoelastic coupling in a correlated itinerant ferromagnet
Author: Marques, Carolina A., Rhodes, Luke C., Osmolska, Weronika, Lane, Harry, Benedii, Izidor, Naritsuka, Masahiro, Berge, Siri A., Fittipaldi, Rosalba, Lettieri, Mariateresa, Vecchione, Antonio, Wahl, Peter
Issue&Volume: 2025-06-17
Abstract: The interaction between the electronic and structural degrees of freedom is central to several intriguing phenomena observed in condensed-matter physics. In magnetic materials, magnetic interactions couple to lattice degrees of freedom, resulting in magnetoelastic coupling, which is typically small and only detectable in macroscopic samples. Here we demonstrate a giant magnetoelastic coupling in the correlated itinerant ferromagnet Sr4Ru3O10. We establish an effective control of magnetism in the surface layer and utilize it to probe the impact of magnetism on its electronic and structural properties. By using scanning tunnelling microscopy, we reveal subtle changes in the electronic structure dependent on ferromagnetic or antiferromagnetic alignment between the surface and subsurface layers. We further determine the consequences of the exchange force on the relaxation of the surface layer, which exhibits giant magnetostriction. Our results provide a direct measurement of the impact of exchange interactions and correlations on structural details in a quantum material, revealing how electronic correlations result in a strong electron–lattice coupling.
DOI: 10.1038/s41567-025-02893-x
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-025-02893-x
