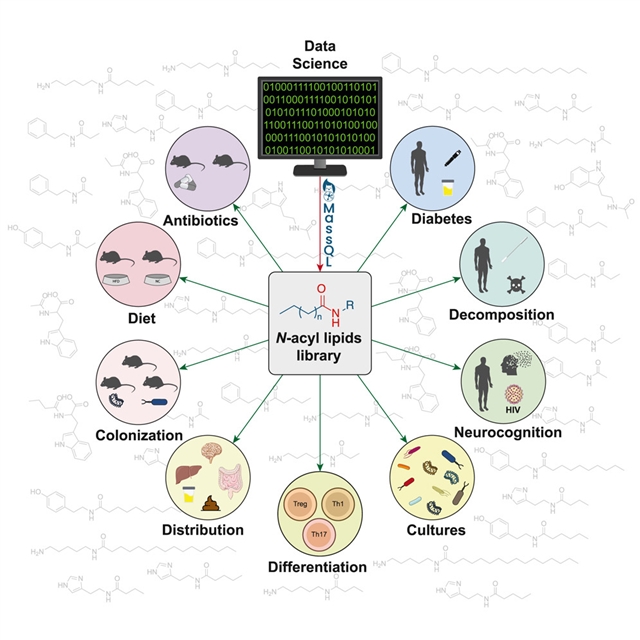
美国加州大学Pieter C. Dorrestein研究组探明了微生物群使长链到短链脂肪酸衍生的N-酰基脂质多样化。这一研究成果于2025年6月10日发表在国际顶尖学术期刊《细胞》上。
为了增强基于非靶向质谱的代谢组学对N-酰基脂质的检测,研究组创建了一个参考谱库,从2700个公共数据集中检索N-酰基脂的模式,确定了851种N-酰基脂质的检测356542次。777种没有在脂质结构数据库中记录,其中18%来自短链脂肪酸,存在于消化道和其他器官中。它们的水平随着饮食和微生物定植以及糖尿病患者而变化。课题组人员将微生物N-酰基脂,包括组胺和多胺偶联物,与HIV状态和认知障碍联系起来。这种抗性将在未来的研究中加强对这些化合物的注释,进一步了解它们在健康和疾病中的作用,并强调大规模非靶向代谢组学数据对代谢物发现的价值。
研究人员表示,N-酰基脂是多种生物过程的重要介质,包括免疫功能和应激反应。
附:英文原文
Title: The microbiome diversifies long- to short-chain fatty acid-derived N-acyl lipids
Author: Helena Mannochio-Russo, Vincent Charron-Lamoureux, Martijn van Faassen, Santosh Lamichhane, Wilhan D. Gonalves Nunes, Victoria Deleray, Adriana V. Ayala, Yuichiro Tanaka, Abubaker Patan, Kyle Vittali, Prajit Rajkumar, Yasin El Abiead, Haoqi Nina Zhao, Paulo Wender Portal Gomes, Ipsita Mohanty, Carlynda Lee, Aidan Sund, Meera Sharma, Yuanhao Liu, David Pattynama, Gregory T. Walker, Grant J. Norton, Lora Khatib, Mohammadsobhan S. Andalibi, Crystal X. Wang, Ronald J. Ellis, David J. Moore, Jennifer E. Iudicello, Donald Franklin, Scott Letendre, Loryn Chin, Corinn Walker, Simone Renwick, Jasmine Zemlin, Michael J. Meehan, Xinyang Song, Dennis Kasper, Zachary Burcham, Jane J. Kim, Sejal Kadakia, Manuela Raffatellu, Lars Bode, Hiutung Chu, Karsten Zengler, Mingxun Wang, Dionicio Siegel, Rob Knight, Pieter C. Dorrestein
Issue&Volume: 2025-06-10
Abstract: N-Acyl lipids are important mediators of several biological processes including immune function and stress response. To enhance the detection of N-acyl lipids with untargeted mass spectrometry-based metabolomics, we created a reference spectral library retrieving N-acyl lipid patterns from 2,700 public datasets, identifying 851 N-acyl lipids that were detected 356,542 times. 777 are not documented in lipid structural databases, with 18% of these derived from short-chain fatty acids and found in the digestive tract and other organs. Their levels varied with diet and microbial colonization and in people living with diabetes. We used the library to link microbial N-acyl lipids, including histamine and polyamine conjugates, to HIV status and cognitive impairment. This resource will enhance the annotation of these compounds in future studies to further the understanding of their roles in health and disease and to highlight the value of large-scale untargeted metabolomics data for metabolite discovery.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.05.015
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell/abstract/S0092-8674(25)00565-3
