Bassem A. Sorbonne UniversitHassan小组取得一项新突破。他们报道了顺序和独立的概率事件调节了黑腹果蝇发育过程中不同的轴突靶向。相关论文发表在2025年5月7日出版的《自然—神经科学》杂志上。
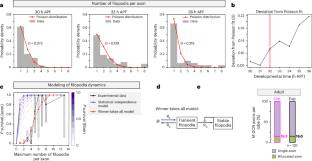
在这项研究中,该课题组研究了果蝇视觉投射神经元DCNs/LC14s的轴突靶向动力学,并对其进行了三维实时成像、数学建模和实验验证。该研究团队发现不同的轴突目标选择是由两个独立的遗传编码随机过程序列驱动的。早期Notch侧抑制将DCNs分离为NotchON近端靶向轴突和NotchOFF轴突,它们采用双电位过渡状态。随后,稳定的微管在一小部分NotchOFF轴突中的概率积累导致远端目标神经支配,而其余的微管则收缩以采用NotchOFF目标选择。顺序连接决定导致每个个体随机选择不同数量的远端目标轴突。总之,这项工作为开发过程中出现单独可变但稳健的电路图提供了一个概念和机制框架。
研究人员表示,大脑线路的变异导致了不可遗传的行为个性。在开发过程中,这些个性化的连接模式是如何以及何时出现并稳定下来的仍未得到探索。
附:英文原文
Title: Sequential and independent probabilistic events regulate differential axon targeting during development in Drosophila melanogaster
Author: Andriatsilavo, Maheva, Barata, Carolina, Reifenstein, Eric, Dumoulin, Alexandre, Tao Griffin, Tian, Dutta, Suchetana Bias, Stoeckli, Esther T., von Kleist, Max, Hiesinger, P. Robin, Hassan, Bassem A.
Issue&Volume: 2025-05-07
Abstract: Variation in brain wiring contributes to non-heritable behavioral individuality. How and when these individualized wiring patterns emerge and stabilize during development remains unexplored. In this study, we investigated the axon targeting dynamics of Drosophila visual projecting neurons called DCNs/LC14s, using four-dimensional live-imaging, mathematical modeling and experimental validation. We found that alternative axon targeting choices are driven by a sequence of two independent genetically encoded stochastic processes. Early Notch lateral inhibition segregates DCNs into NotchON proximally targeting axons and NotchOFF axons that adopt a bi-potential transitory state. Subsequently, probabilistic accumulation of stable microtubules in a fraction of NotchOFF axons leads to distal target innervation, whereas the rest retract to adopt a NotchON target choice. The sequential wiring decisions result in the stochastic selection of different numbers of distally targeting axons in each individual. In summary, this work provides a conceptual and mechanistic framework for the emergence of individually variable, yet robust, circuit diagrams during development.
DOI: 10.1038/s41593-025-01937-y
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-025-01937-y
Nature Neuroscience:《自然—神经科学》,创刊于1998年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:28.771
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/neuro/
投稿链接:https://mts-nn.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
