中国科学院上海药物研究所冷颖研究小组在研究中取得进展。他们报道了茯苓三萜类化合物脱氢三苯甲醇甲酯通过靶向Caspase-1抑制小鼠NLRP3炎性小体活化,缓解非酒精性脂肪性肝炎。该项研究成果发表在2025年5月6日出版的《中国药理学报》上。
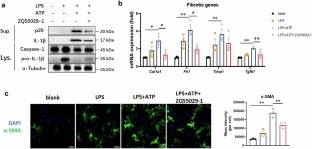
在这项研究中,该研究团队研究了脱氢曲烯酸甲酯(ZQS5029-1)在高脂肪饮食中CCl4诱导的小鼠NASH模型和GAN饮食诱导的ob/ob小鼠NASH模型中的治疗作用。NASH小鼠分别接受ZQS5029-1(75mg·kg-1·d-1,i.g.)治疗6周和8周。该课题组发现ZQS5029-1治疗明显减轻了两种小鼠NASH模型的肝损伤、炎症和纤维化。该课题组研究人员发现,ZQS5029-1治疗显著抑制了NASH小鼠模型中肝脏NOD-、LRR-和pyrin结构域蛋白3 (NLRP3)炎性体的激活,并在体外阻断了骨髓源性巨噬细胞(BMDMs)和Kupffer细胞中脂多糖(LPS)+腺苷5 ' -三磷酸(ATP)/ Nigericin诱导的NLRP3炎性体的激活。研究组证明ZQS5029-1直接结合到motheme Caspase-1的H236残基上,从而抑制NLRP3炎性体的激活。使用LPS预处理的巨噬细胞上清液分析ZQS5029-1对巨噬细胞-肝细胞/HSC串扰的影响 + ATP导入肝细胞和肝星状细胞(HSCs)。该团队发现来自BMDMs的条件培养基诱导损伤和死亡,以及肝细胞中的脂质积累和HSCs的激活;这些效应被ZQS5029-1处理的BMDMs的条件培养基阻断。
此外,ZQS5029-1对肝细胞和HSCs的保护作用被Caspase-1的H236A突变所消除。课题组得出结论,ZQS5029-1通过靶向Caspase-1和调节巨噬细胞-肝细胞/HSCs串扰抑制NLRP3炎性体激活,是治疗NASH的有希望的先导化合物。
据介绍,非酒精性脂肪性肝炎(NASH)已成为一种普遍存在的慢性肝病,临床需求尚未得到满足。少数研究报道了茯苓提取物对NASH小鼠的有益作用,但其有效成分尚不清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: Dehydrotrametenolic acid methyl ester, a triterpenoid of Poria cocos, alleviates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation via targeting Caspase-1 in mice
Author: Xia, Ling-yan, Yu, Nai-rong, Huang, Su-ling, Qu, Hui, Qin, Li, Zhao, Qin-shi, Leng, Ying
Issue&Volume: 2025-05-06
Abstract: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) has emerged as a prevalent chronic liver disease with a huge unmet clinical need. A few studies have reported the beneficial effects of Poria cocos Wolf (P. cocos) extract on NASH mice, but the active components were still unknown. In this study we investigated the therapeutic effects of dehydrotrametenolic acid methyl ester (ZQS5029-1), a lanosterol-7,9(11)-diene triterpenes in P. cocos, in a high-fat diet plus CCl4 induced murine NASH model and a GAN diet induced ob/ob murine NASH model. The NASH mice were treated with ZQS5029-1 (75mg·kg–1·d–1, i.g.) for 6 and 8 weeks, respectively. We showed that ZQS5029-1 treatment markedly relieved liver injury, inflammation and fibrosis in both the murine NASH models. We found that ZQS5029-1 treatment significantly suppressed hepatic NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation in both the NASH murine models, and blocked lipopolysaccharides (LPS)+adenosine 5’-triphosphate (ATP)/Nigericin-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation in bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) and Kupffer cells in vitro. We demonstrated that ZQS5029-1 directly bound to the H236 residue of mouse Caspase-1, thereby inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. The effects of ZQS5029-1 on macrophage-hepatocyte/HSC crosstalk were analyzed using the supernatants from macrophages preconditioned with LPS+ATP introduced into hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). We found that the conditioned medium from the BMDMs induced injury and death, as well as lipid accumulation in hepatocytes, and activation of HSCs; these effects were blocked by conditioned medium from BMDMs treated with ZQS5029-1. Moreover, the protective effects of ZQS5029-1 on hepatocytes and HSCs were eliminated by H236A-mutation of Caspase-1. We conclude that ZQS5029-1 is a promising lead compound for the treatment of NASH by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation through targeting Caspase-1 and regulating the macrophage-hepatocyte/HSC crosstalk.
DOI: 10.1038/s41401-025-01569-9
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41401-025-01569-9
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica:《中国药理学报》,创刊于1980年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:8.2
官方网址:http://www.chinaphar.com/
投稿链接:https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/aphs
