中国科学技术大学免疫学研究所田志刚研究团队在研究中取得进展。他们揭示了CD200R阻断通过释放肿瘤中的NK和CD8+T细胞增强抗肿瘤免疫。这一研究成果发表在2025年5月6日出版的国际学术期刊《中国药理学报》上。
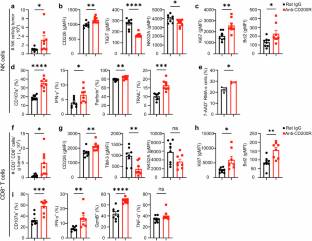
在本研究中,该课题组探讨了靶向CD200R在肿瘤免疫治疗中的治疗潜力和细胞机制。该课题组研究人员建立了4个以MC38(结肠癌)、MCA205(纤维肉瘤)、LLC(肺癌)和EO771(乳腺癌)细胞系为主题的皮下肿瘤模型。研究团队发现CD200R在具有衰竭表型的NK细胞和CD8+ T细胞的皮下肿瘤模型中高度表达。无论是基因消融还是抗体阻断CD200R,都可以通过阻止或逆转NK细胞和CD8+ T细胞的衰竭来延缓肿瘤生长,延长荷瘤小鼠的生存期。CD200R抗体与抗PD-1/抗PD- l1联合治疗可协同抑制肿瘤生长。通过消耗NK或/和CD8+ T细胞,该课题组人员证明这两种细胞类型都有助于CD200R阻断在荷瘤小鼠中的抗肿瘤功效。此外,阻断人CD200R可显著增强人NK细胞功能,抑制PBMC重组异种移植小鼠的肿瘤生长。他们的研究结果表明,CD200R是一种潜在的免疫检查点分子,可以抑制NK细胞和CD8+ T细胞的杀肿瘤活性,并且可以在未来作为治疗靶点加以利用。
据介绍,免疫检查点抑制剂已经彻底改变了癌症治疗,但很大一部分患者对目前的检查点免疫疗法反应不佳。CD200R(又称OX2R)是免疫球蛋白超家族中的一种跨膜糖蛋白,主要表达于髓细胞、自然杀伤细胞(NK)和CD8+ T细胞等髓细胞和淋巴细胞来源的免疫能力细胞。
附:英文原文
Title: CD200R blockade enhances anti-tumor immunity by unleashing NK and CD8+ T cells in tumor
Author: Zhang, Zheng-feng, Zhang, Yu, Chen, Ya-wen, Cao, Guo-shuai, Zheng, Xiao-dong, Sun, Rui, Peng, Hui, Tian, Zhi-gang, Sun, Hao-yu
Issue&Volume: 2025-05-06
Abstract: Immune checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized cancer therapy, but a large proportion of patients do not respond well to current checkpoint immunotherapies. CD200R (also known as OX2R) is a transmembrane glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin superfamily that is mainly expressed on myeloid and lymphoid-derived immunocompetent cells such as myeloid cells, natural killer (NK), and CD8+ T cells. In this study, we investigated the therapeutic potential and cellular mechanisms of targeting CD200R in tumor immunotherapy. We established 4 subcutaneous tumor mouse models using MC38 (colon cancer), MCA205 (fibrosarcoma), LLC (lung cancer), and EO771 (mammary cancer) cell lines. We found that CD200R was highly expressed on tumor-infiltrating NK and CD8+ T cells with exhausted phenotypes in the four subcutaneous tumor mouse models. Either genetic ablation or antibody blockade of CD200R retarded tumor growth and prolonged the survival of tumor-bearing mice by preventing or reversing exhaustion of both NK cells and CD8+ T cells. The combined therapy of CD200R antibody with anti-PD-1/anti-PD-L1 synergistically inhibited tumor growth. By depletion of NK or/and CD8+ T cells, we demonstrated that both cell types contributed to the anti-tumor efficacy of CD200R blockade in tumor-bearing mice. Further, the blockade of human CD200R significantly enhanced human NK cell function and inhibited human tumor growth in PBMC-reconstituted xenograft mice. Our results demonstrate that CD200R is a potential immune checkpoint molecule that can suppress the tumoricidal activities of NK and CD8+ T cells, and could thus be exploited as a therapeutic target in the future.
DOI: 10.1038/s41401-025-01556-0
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41401-025-01556-0
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica:《中国药理学报》,创刊于1980年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:8.2
官方网址:http://www.chinaphar.com/
投稿链接:https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/aphs
