内质网Nogo驱动AgRP神经元的激活和摄食行为,这一成果由哥伦比亚大学Sabrina Diano研究小组经过不懈努力而取得。2025年5月6日出版的《细胞—代谢》杂志发表了这一最新研究成果。
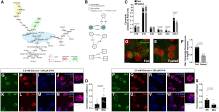
课题组发现Nogo-A由网状蛋白4 (Rtn4)基因编码,与大脑发育和突触可塑性相关,通过控制Agouti相关蛋白(AgRP)神经元的脂质代谢来调节摄食和能量代谢。禁食小鼠AgRP神经元中Nogo-A的表达上调,并与鞘脂新生生物合成相关酶的显著下调以及细胞内脂质转运和脂肪酸氧化关键酶的上调有关。AgRP神经元中Rtn4的缺失减少了体重、胃饥饿素诱导的AgRP活性和食物摄入量,以及禁食诱导的AgRP激活,同时神经酰胺水平升高。最后,高脂肪饮食诱导的肥胖诱导AgRP神经元中Rtn4的显著下调和神经酰胺水平的升高,提示Nogo在肥胖中AgRP失调中的作用。综上所述,他们的数据显示Nogo-A通过控制线粒体功能和细胞脂质代谢来驱动AgRP神经元活动和相关的摄食行为。
据悉,下丘脑的脂质感知有助于控制摄食和全身代谢。然而,负责这种营养感知过程的机制是不明确的。
附:英文原文
Title: Endoplasmic reticulum Nogo drives AgRP neuronal activation and feeding behavior
Author: Sungho Jin, Nal Ae Yoon, Mian Wei, Tilla Worgall, Luisa Rubinelli, Tamas L. Horvath, Wei Min, Nadia Diano, Annarita di Lorenzo, Sabrina Diano
Issue&Volume: 2025-05-06
Abstract: Lipid sensing in the hypothalamus contributes to the control of feeding and whole-body metabolism. However, the mechanism responsible for this nutrient-sensing process is ill-defined. Here, we show that Nogo-A, encoded by reticulon 4 (Rtn4) gene and associated with brain development and synaptic plasticity, regulates feeding and energy metabolism by controlling lipid metabolism in Agouti-related protein (AgRP) neurons. Nogo-A expression was upregulated in AgRP neurons of fasted mice and was associated with a significant downregulation of enzymes involved in sphingolipid de novo biosynthesis and the upregulation of key enzymes in intracellular lipid transport and fatty acid oxidation. Deletion of Rtn4 in AgRP neurons reduced body weight, ghrelin-induced AgRP activity and food intake, and fasting-induced AgRP activation, together with an increase in ceramide levels. Finally, high-fat-diet-induced obesity induced a significant downregulation of Rtn4 and increased ceramide levels in AgRP neurons, suggesting a role for Nogo in AgRP dysregulation in obesity. Taken together, our data reveal that Nogo-A drives AgRP neuronal activity and associated feeding behavior by controlling mitochondrial function and cellular lipid metabolism.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2025.04.005
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(25)00215-3
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
