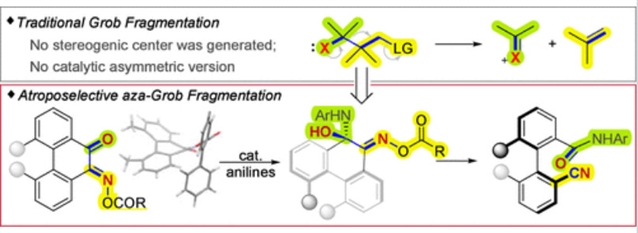
近日,中国科学技术大学顾振华团队研究了催化不对称选择性氮杂Grob裂解:一种轴向手性双芳腈的方法。该项研究成果发表在2025年5月6日出版的《美国化学会杂志》上。
Grob裂解是一种切割C-C键的强大合成工具,在构建七至九元碳环或杂环方面特别有用。这种反应通常会破坏一个C-C键和一个C-X键,形成两个不饱和官能团。由于没有产生立体中心,催化不对称Grob裂解尚未得到探索。在这项研究中,课题组成功开发了α-酮肟酯的催化不对称氮杂Grob裂解,实现了阿曲波选择性C-C键裂解,构建了轴向手性联芳腈。
肟酯的单晶X射线衍射分析阐明了结构-反应性关系,突出了扭转应变的作用。这些研究还揭示了2-苯基苯甲酰基在控制底物构象、调节反应性和立体选择性方面的独特作用。1H NMR滴定实验提供了催化剂与底物活化模式的简要见解,表明了多氢键相互作用模型。
附:英文原文
Title: Catalytic Atroposelective aza-Grob Fragmentation: An Approach toward Axially Chiral Biarylnitriles
Author: Lin Li, Linlin Ding, Xue Zhang, Chengnuo Zhang, Minyan Wang, Zhenhua Gu
Issue&Volume: May 6, 2025
Abstract: Grob fragmentation is a powerful synthetic tool for cleaving C–C bonds, which was particularly useful in the construction of seven- to nine-membered carbocycles or heterocycles. This reaction typically breaks one C–C bond and one C–X bond and forms two unsaturated functional groups. As no stereogenic centers are generated, catalytic asymmetric Grob fragmentation has remained unexplored. In this study, we have successfully developed a catalytic asymmetric aza-Grob fragmentation of α-keto oxime esters, achieving atroposelective C–C bond cleavage to construct axially chiral biarylnitriles. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis of oxime esters elucidated the structure–reactivity relationship, highlighting the role of torsional strain. These studies also revealed the unique role of the 2-phenyl benzoyl group in controlling the substrate conformation, tuning reactivity, and stereoselectivity. The 1H NMR titration experiments provided brief insights into the activation mode of the catalyst with the substrate, suggesting a multi-hydrogen-bonding interaction model.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c02978
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c02978
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
