近日,美国加州大学圣地亚哥分校Suckjoon Jun团队研究了体内Min蛋白稳健且资源最优的动态模式形成。这一研究成果于2025年5月5日发表在《自然—物理学》杂志上。
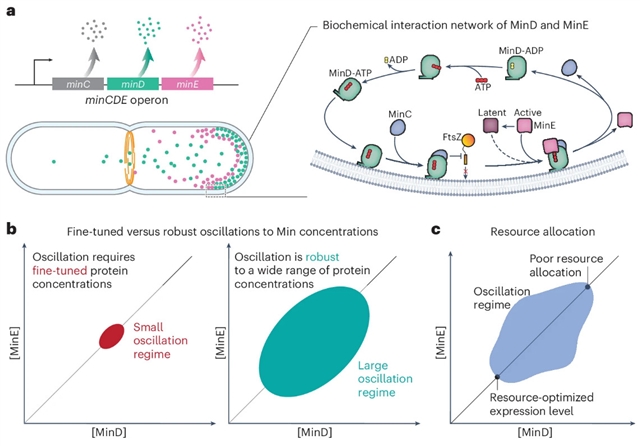
Min蛋白系统通过在细胞极之间形成振荡模式来防止细菌中的异常细胞分裂。然而,预测振荡开始时的蛋白质浓度以及细胞是否能在生理扰动下维持振荡仍然具有挑战性。研究组表明,使用基因工程大肠杆菌菌株,动态模式形成在广泛的Min蛋白水平和生长生理变化范围内是稳健的。研究组在快速和缓慢生长条件下调节minCD和minE的表达,并构建了MinD与minE相图,揭示了动态模式,包括行波和驻波。
结果发现Min蛋白的自然表达水平是资源最优的,并且对蛋白质浓度的变化具有鲁棒性。此外,他们在相图上观察到动态Min模式的不变波长。用基于反应扩散模型的生物物理学理论定量解释了实验结果,该模型考虑了MinE在其潜在状态和活性状态之间的切换,表明了它作为体内Min振荡鲁棒性模块的重要作用。该研究结果强调了整合定量细胞生理学和生物物理建模以了解控制细胞分裂机制的基本机制的潜力,并提供了适用于其他生物过程的见解。
附:英文原文
Title: Robust and resource-optimal dynamic pattern formation of Min proteins in vivo
Author: Ren, Ziyuan, Weyer, Henrik, Sandler, Michael, Wrthner, Laeschkir, Fu, Haochen, Tangtartharakul, Chanin B., Li, Dongyang, Sou, Cindy, Villarreal, Daniel, Kim, Judy E., Frey, Erwin, Jun, Suckjoon
Issue&Volume: 2025-05-05
Abstract: The Min protein system prevents abnormal cell division in bacteria by forming oscillatory patterns between cell poles. However, predicting the protein concentrations at which oscillations start and whether cells can maintain them under physiological perturbations remains challenging. Here we show that dynamic pattern formation is robust across a wide range of Min protein levels and variations in the growth physiology using genetically engineered Escherichia coli strains. We modulate the expression of minCD and minE under fast- and slow-growth conditions and build a MinD versus MinE phase diagram that reveals dynamic patterns, including travelling and standing waves. We found that the natural expression level of Min proteins is resource-optimal and robust to changes in protein concentration. In addition, we observed an invariant wavelength of dynamic Min patterns across the phase diagram. We explain the experimental findings quantitatively with biophysical theory based on reaction–diffusion models that consider the switching of MinE between its latent and active states, indicating its essential role as a robustness module for Min oscillation in vivo. Our results underline the potential of integrating quantitative cell physiology and biophysical modelling to understand the fundamental mechanisms controlling cell division machinery, and they offer insights applicable to other biological processes.
DOI: 10.1038/s41567-025-02878-w
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-025-02878-w
