浙江理工大学Lingyu Shao团队近日研究了颗粒凝聚生长过程中非均相成核与非均相成核的竞争效应。相关论文于2025年5月22日发表在《颗粒学报》杂志上。
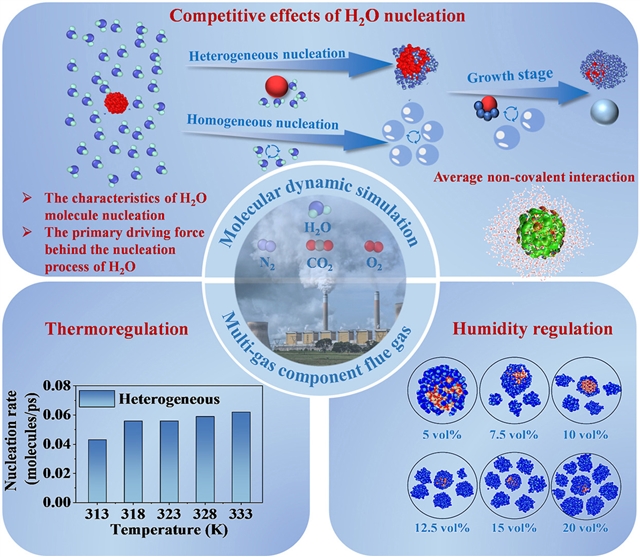
提高燃煤电厂排放细颗粒物去除效率的主要方法包括应用水蒸气相变预处理技术。研究组利用分子动力学(MD)模拟来研究多气体组成条件下细颗粒与H2O之间的非均匀成核过程。结果表明,H2O的非均匀成核和均匀成核过程同时发生,两者之间存在竞争关系。
H2O在颗粒上的成核过程以特定位点的形成为特征。在这些区域,H2O通过氢键与颗粒表面上的O原子强烈相互作用,导致这些位点附近的优先冷凝。温度对颗粒生长的影响主要涉及H2O的相互作用和自扩散过程。
随着温度的降低,颗粒的尺寸先增加后减小,在323 K时达到最大值。与温度变化的影响相反,H2O含量对细颗粒生长的影响主要表现为H2O分子的均匀成核和非均匀成核之间的竞争。这些发现,包括细颗粒的成核特性和气体温度和湿度的影响机制,加强了水蒸气相变技术的理论体系,促进了燃煤烟气中细颗粒的去除,并为后续工艺优化提供了理论支持。
附:英文原文
Title: Competitive effects between heterogeneous and homogeneous nucleation during particle condensation growth process
Author: Zhengda Yang , Lingyu Shao
Issue&Volume: 2025/05/22
Abstract: The principal method for improving the removal efficiency of fine particles emitted from coal-fired power plants involves the application of water vapor phase change pretreatment technology. This study utilizes molecular dynamic (MD) simulation to examine the heterogeneous nucleation process between fine particles and H2O under conditions of multi-gas composition. Results showed that the heterogeneous nucleation and the homogeneous nucleation process of H2O occur concurrently, with both processes engaged in a competitive relationship. The nucleation process of H2O on particles is characterized by the formation of specific sites. In these regions, H2O interacts strongly with the O atoms on the particle surface through hydrogen bonding, leading to preferential condensation in the vicinity of these sites. The influence of temperature on particle growth primarily involves interaction and self-diffusion processes of H2O. As the temperature decreases, the size of particles initially increases and then decreases, reaching a maximum at 323 K. In contrast to the effects of temperature change, the influence of H2O content on fine particulate growth is primarily characterized by the competition between homogeneous and heterogeneous nucleation of H2O molecules. These findings, including the nucleation characteristics of fine particles and the influence mechanism of gas temperature and humidity, strengthen the theoretical system of water vapor phase change technology to promote the removal of fine particles from coal-fired flue gas, and provide theoretical support for subsequent process optimization.
DOI: 10.1016/j.partic.2025.05.011
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1674200125001385
Particuology:《颗粒学报》,创刊于2003年。隶属于爱思唯尔出版集团,最新IF:3.5
官方网址:https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/particuology
投稿链接:https://www2.cloud.editorialmanager.com/partic/default2.aspx
