近日,瑞士苏黎世联邦理工学院Gabriele Rainò团队研究了CsPbBr3钙钛矿量子点的单光子超吸收。2025年5月21日,《自然—光子学》期刊发表了这一成果。
通过带间光学跃迁吸收光在自然界和应用技术中起着关键作用,可以实现高效的光合作用和光伏电池、快速光电探测器或敏感的(量子)光-物质界面。在许多这样的光子系统中,增强光吸收强度将有利于产生更高的器件效率和增强的速度或灵敏度。然而,到目前为止,无腔光吸收体的可工程吸收率很低,这与初始状态和最终状态之间的耦合强度是固有材料参数的概念是一致的。相比之下,理论上预测了超辐射系统的吸收率大大提高,该系统通过电子极化的空间扩展相干振荡具有巨大的振子强度。然而,与发射过程不同,吸收中超辐射的实验实现——“超吸收”——仍然很稀疏,需要复杂的激发态工程方法。
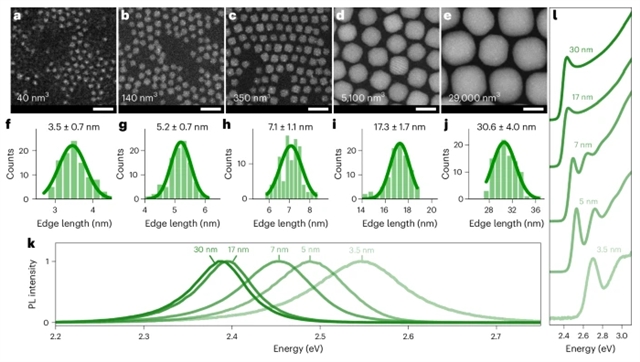
研究组报告了大CsPbBr3钙钛矿量子点中单光子超辐射的时间反转的超吸收。光谱学揭示了带隙吸收随量子点体积的增加而强烈增加,这与巨激子波函数一致。构型相互作用计算与实验定量一致,将观察到的单光子超吸收归因于强电子-空穴对状态相关性。该方法为开发更高效的光电器件和量子光-物质界面带来了新的机遇。
附:英文原文
Title: Single-photon superabsorption in CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots
Author: Boehme, Simon C., Nguyen, Tan P. T., Zhu, Chenglian, Cherniukh, Ihor, Feld, Leon G., Dirin, Dmitry N., Bodnarchuk, Maryna I., Katan, Claudine, Even, Jacky, Kovalenko, Maksym V., Rain, Gabriele
Issue&Volume: 2025-05-21
Abstract: The absorption of light via interband optical transitions plays a key role in nature and applied technology, enabling efficient photosynthesis and photovoltaic cells, fast photodetectors or sensitive (quantum) light–matter interfaces. In many such photonic systems, enhancing the light absorption strength would be beneficial for yielding higher device efficiency and enhanced speed or sensitivity. So far, however, cavity-free light absorbers feature poorly engineerable absorption rates, consistent with the notion that the coupling strength between the initial and final states is an intrinsic material parameter. By contrast, greatly enhanced absorption rates had been theoretically predicted for superradiant systems, which feature giant oscillator strength through spatially extended coherent oscillations of the electron polarization. Unlike for emission processes, however, experimental realizations of superradiance in absorption—‘superabsorption’—remain sparse and require complicated excited-state engineering approaches. Here we report superabsorption by the time reversal of single-photon superradiance in large CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots. Optical spectroscopy reveals a bandgap absorption that strongly increases with the quantum dot volume, consistent with a giant exciton wavefunction. Configuration-interaction calculations, quantitatively agreeing with the experiment, attribute the observed single-photon superabsorption to strong electron–hole pair-state correlations. The approach brings new opportunities for the development of more efficient optoelectronic devices and quantum light–matter interfaces.
DOI: 10.1038/s41566-025-01684-3
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-025-01684-3
