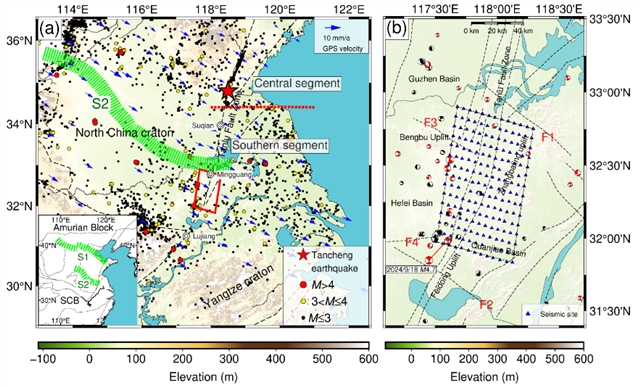
近日,中国科学技术大学张海江团队发现环境噪声层析成像揭示了郯庐断裂带张巴岭段上地壳广泛分布的北西向隐伏断裂。2025年5月20日出版的《中国科学:地球科学》杂志发表了这项成果。
郯庐断裂带(TLFZ)被认为是中国东部最大的活动走滑断裂系统,其各段具有明显的构造特征和地震活动。为了阐明TLFZ张八岭隆起(ZBU)段上地壳和中地壳的结构特征,研究组采用了2020年部署的由192个节点组成的密集地震阵列收集的环境噪声数据。利用环境噪声层析成像,他们推导出了该区域的三维S波速度(Vs)结构,延伸到10公里。
断层扫描结果显示,在0-2公里深度处存在明显的低速异常?断层带沿线处,与断层地堑结构相关。根据Vs特征,张八岭北部的明光地堑延伸至3公里,而在南部的合肥盆地东翼,它达到1.5公里。此外,在3-5公里的深度处发现了几个西北走向的低速条纹,位于蚌埠隆起和合肥盆地东侧,可能对应于NW走向的左侧隐伏断层。
通过整合区域速度结构、地表GPS方向和地震震源机制,研究组提出了TLFZ张八岭段的构造模型。该模型表明,NW向隐伏断层可能在调节TLFZ上的近东西向应力载荷方面发挥关键作用。
附:英文原文
Title: Ambient noise tomography reveals widely distributed NW-trending hidden faults in the upper crust of the Zhangbaling segment of the Tanlu Fault Zone
Author: Ji GAO, Haijiang ZHANG, Yuqi HUANG, Jiawei QIAN, Tian ZHAO, Lingli LI
Issue&Volume: 2025/05/20
Abstract: The Tanlu Fault Zone (TLFZ), recognized as the largest active strike-slip fault system in eastern China, exhibits distinct structural features and seismic activities across its various segments. To elucidate the structural characteristics of the upper and middle crust in the Zhangbaling Uplift (ZBU) segment of the TLFZ, we employed ambient noise data collected from a dense seismic array comprising 192 nodes, deployed in 2020. Utilizing ambient noise tomography, we derived a three-dimensional S-wave velocity (Vs) structure of the region, extending to a depth of 10km. The tomographic results reveal a prominent low-velocity anomaly at depths of 0–2km along the fault zone, which correlates with the fault graben structure. According to the Vs characteristics, the Mingguang Graben in the northern part of Zhangbaling extends to a depth of 3km, whereas on the eastern flank of the Hefei Basin in the south, it reaches 1.5km. Additionally, several NW-trending low-velocity stripes are identified at depths of 3–5km on the eastern side of the Bengbu Uplift and the Hefei Basin, likely corresponding to NW-trending left-lateral hidden faults. By integrating the regional velocity structure, surface GPS directions, and earthquake focal mechanisms, we proposed a tectonic model for the Zhangbaling segment of the TLFZ. This model suggests that the NW-trending hidden faults may play a crucial role in modulating the near east-west stress loading on the TLFZ.
DOI: 10.1007/s11430-024-1557-8
Source: https://www.sciengine.com/SCES/doi/10.1007/s11430-024-1557-8
Science China Earth Sciences:《中国科学:地球科学》,创刊于1952年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:5.7
官方网址:https://www.sciengine.com/SCES/home
投稿链接:https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/sces
