近日,南京大学王海鲲团队研究了夜间气温异常的时空变化趋势及其大气机制。该研究于2025年5月21日发表在《中国科学:地球科学》杂志上。
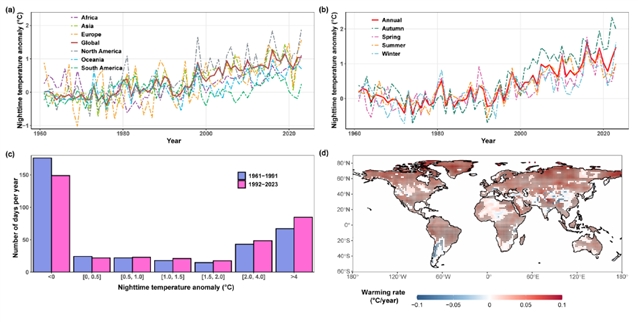
近几十年来,全球气温迅速上升,不同地区夜间的变暖速度高于白天。夜间异常高温可能对人类健康和社会构成额外风险。然而,世界各地对夜间温度异常的时空趋势和局部大气机制的研究较少。课题组研究了1961年至2023年夜间温度异常(NTA)的时空趋势,并分析了与不同程度的正温度异常相关的潜在物理机制。
结果发现,NTA在全球范围内呈显著增长趋势,增长率为0.21°C/10年。在大陆范围内,北美、亚洲和欧洲的NTA增长更快。正NTA的发生通常与局部云层覆盖、降水和湿度的增加有关,这有助于增强夜间的下行长波辐射和温室效应。在年际尺度上,NTA与前一个冬季海洋厄尔尼诺指数呈正相关,表明厄尔尼诺-南方涛动可能对全球夜间温度产生调节作用。该研究结果有助于了解近几十年来夜间异常温度的变化和影响机制,并为炎热夜晚的预测和应对提供信息。
附:英文原文
Title: Spatiotemporal trend of nighttime temperature anomaly and its atmospheric mechanism
Author: Bowen CHU, Jianfeng LUO, Haikun WANG
Issue&Volume: 2025/05/21
Abstract: Global temperature has increased at a rapid rate in recent decades, and the warming rate at night is observed higher than that during the daytime among different regions. Nighttime anomalous high temperatures may pose an additional risk to human health and society. Nevertheless, less research has explored the spatiotemporal trend and the local atmospheric mechanism of nocturnal temperature anomaly around the world. Here, we investigate the spatiotemporal trend of nighttime temperature anomaly (NTA) from 1961 to 2023, and analyze the underlying physical mechanism related to different extents of positive temperature anomaly. We find that NTA showed a significantly increased trend worldwide, with an increasing rate of 0.21°C/decade. At the continental scale, NTA has increased faster in North America, Asia, and Europe. The occurrence of positive NTA is generally associated with local increased cloud cover, precipitation, and humidity, which contribute to enhanced downward longwave radiation and greenhouse effect at night. On the inter-annual scale, NTA is positively related to the preceding winter Oceanic Nio Index, indicating the possible modulation of El Nio-Southern Oscillation on the global nocturnal temperature. Our results could help to understand the variation and influence mechanism of anomalous nighttime temperature in recent decades, and inform the forecast of and response to hot nights.
DOI: 10.1007/s11430-024-1570-5
Source: https://www.sciengine.com/SCES/doi/10.1007/s11430-024-1570-5
Science China Earth Sciences:《中国科学:地球科学》,创刊于1952年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:5.7
官方网址:https://www.sciengine.com/SCES/home
投稿链接:https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/sces
