温州医科大学罗武研究小组的一项最新研究揭示了OTUD1缺乏通过调节RACK1磷酸化来减轻心肌缺血/再灌注诱导的心肌细胞凋亡。该项研究成果发表在2025年5月20日出版的《中国药理学报》上。
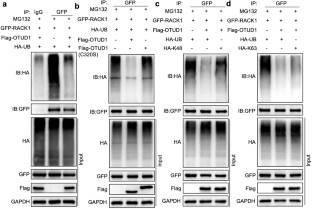
本研究探讨卵巢肿瘤去泛素酶1 (OTUD1)在I/R诱导心肌损伤中的作用及分子机制。研究发现,心肌OTUD1在I/R诱导的心脏组织中表达上调,OTUD1的整体缺失可显著改善I/R诱导的心肌损伤和功能障碍。同样,沉默或过表达OTUD1会影响缺氧/再氧化(H/R)诱导的培养心肌细胞凋亡。机制上,免疫沉淀-质谱分析显示OTUD1直接结合活化C-激酶1受体(RACK1),该受体已被鉴定为多种激酶的支架蛋白,包括丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPKs)和核因子κ B激酶抑制剂(IKK)。OTUD1可以切割K63连接的多泛素链,从而增强RACK1的磷酸化,从而调节MAPKs和核因子κB (NF-κB)信号。最后,RACK1的沉默逆转了OTUD1促进的H/R诱导的心肌凋亡。总之,他们的研究结果表明OTUD1通过去泛素化RACK1促进I/R诱导的心脏损伤,这表明OTUD1是心肌I/R的潜在治疗靶点。
据介绍,心肌梗死(MI)是心血管疾病(CVD)的重要危险因素,其发病率在全球范围内呈上升趋势。心肌缺血再灌注(I/R)损伤常见于缺血心肌。近年来的研究表明,泛素化在心脏病理生理过程中起着重要的作用。
附:英文原文
Title: OTUD1 deficiency attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by regulating RACK1 phosphorylation
Author: Luo, Yue, Li, Wei-xin, Zheng, Qing-song, Yan, Jue-qian, Yang, Yu-die, Shen, Si-rui, Zhang, Qian-hui, Liang, Guang, Wang, Yi, Chen, Ding-dao, Hu, Xiang, Luo, Wu
Issue&Volume: 2025-05-20
Abstract: Myocardial infarction (MI) is an important risk factor of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and its incidence has been on the rise globally. Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury is frequently detected in the ischemic myocardium. Recent studies have shown that ubiquitination plays an important role in the cardiac pathophysiological processes. Herein, we investigated the role and molecular mechanism of Ovarian tumor deubiquitinase 1 (OTUD1) in I/R induced myocardial injury. It was observed that the myocardial OTUD1 was upregulated in I/R-induced heart tissues and global deletion of OTUD1 significantly ameliorated I/R induced myocardial injury and dysfunction. Similarly, silencing or overexpression OTUD1 affected the hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) induced cell apoptosis in cultured cardiomyocytes. Mechanistically, immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry revealed that OTUD1 directly bound to receptor for activated C-kinase 1 (RACK1) which has been identified as a scaffold protein for multiple kinases including mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPKs) and Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase (IKK). OTUD1 could cleave K63-linked polyubiquitin chains to enhance RACK1 phosphorylation, thus modulating MAPKs and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling. Finally, silencing of RACK1 reverses OTUD1-promoted H/R induced myocardial apoptosis. In conclusion, our findings suggest that OTUD1 promotes I/R-induced heart injury by deubiquitinating RACK1, suggesting that OTUD1 is a potential therapeutic target for myocardial I/R.
DOI: 10.1038/s41401-025-01567-x
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41401-025-01567-x
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica:《中国药理学报》,创刊于1980年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:8.2
官方网址:http://www.chinaphar.com/
投稿链接:https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/aphs
