南京工业大学黄维团队近期研究了一种多用途的吩硒肼荧光粉的高效有机机械磷光。2025年5月19日出版的《美国化学会志》发表了这项成果。
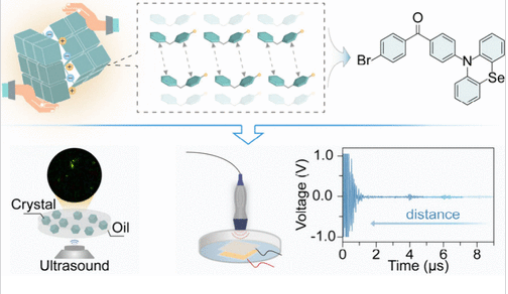
具有磷光特性的机械发光(ML)材料在压力传感和材料损伤检测方面具有巨大的应用潜力。然而,目前报道的机械荧光(MP)材料存在发光效率低和亮度不足的问题。研究组报告了一种压电材料p-BPM,其磷光效率极高,为61.4%,是报告的纯有机MP材料中最高的值。得益于其出色的ML性能,他们开发了一种使用晶体的显示设备,可以清晰地观察书写的字母路径(字母M和L),这在压敏显示器中具有广阔的前景。
令人惊讶的是,研究组还观察到,在低超声工作频率(40kHz)下,晶体在介质中产生明亮的超声诱导发光。晶体和聚对苯二甲酸丁二醇酯(PBAT)聚合物的复合薄膜在保持有效MP的同时表现出显著的拉伸强度。复合薄膜显示出良好的压电能量收集性能,最大开路电压为0.47 V,短路电流为0.046μa,显示出精确声定位的前景。 这项工作将促进高效有机MP材料的开发,扩大应力监测、成像和海洋机器人的潜力。
附:英文原文
Title: High-Efficiency Organic Mechanophosphorescence from A Phenoselenazine Phosphor for Multiple Applications
Author: Meijuan Ding, Meng Zhang, Anqi Lv, Qiuzhuo Dong, Yi Zhang, Wei Li, Zhongfu An, Wei Huang
Issue&Volume: May 19, 2025
Abstract: Mechanoluminescence (ML) materials with phosphorescent characteristics hold significant potential for applications in pressure sensing and material damage inspection. However, currently reported mechanophosphorescence (MP) materials suffer from low luminescence efficiency and insufficient brightness. Herein, we report a piezoelectric material, p-BPM, with an exceptionally high phosphorescence efficiency of 61.4%, which is the highest value among reported pure organic MP materials. Benefiting from its excellent ML performance, we have developed a display device using crystals that allow for clear observation of the written letter paths (letters M and L), which have promising prospects in pressure-sensitive display. Amazingly, we also observed that the crystals produce bright ultrasound induced luminescence in the medium at a low ultrasonic operating frequency (40 kHz). The composite films of crystal and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) polymer exhibit significant tensile strength while maintaining effective MP. The composite films show good piezoelectric energy harvesting properties with a maximum open-circuit voltage of 0.47 V and short-circuit current of 0.046 μA, demonstrating promise for precise sonic location. This work will facilitate the development of highly efficient organic MP materials, expanding the potential in stress-monitoring, imaging, and marine robotics.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c17418
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.4c17418
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
