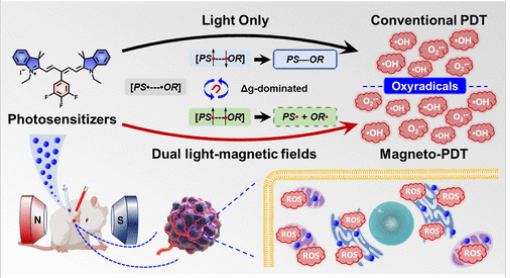
近日,大连理工大学樊江莉团队研究了光动力中间体的自旋操纵工程:磁性放大氧自由基的产生以增强抗肿瘤光疗疗效。这一研究成果于2025年5月13日发表在《美国化学会杂志》上。
提高光敏化效率是光动力疗法(PDT)研究中的一个关键挑战。虽然花青素因其大的消光系数和优异的生物相容性而显示出作为光敏剂(PS)的潜力,但系统间交叉的固有局限性严重影响了治疗效果。研究组提出了一种自下而上的磁增强光动力疗法(磁PDT)范式,该范式采用氟苯取代的五甲川菁作为I型活性氧生成剂。
基于自由基对机制和磁场效应,PS和氧自由基之间的g因子(Δg)的显著差异使得Cy5–3,4,5–3介导的羟基自由基(·OH)和超氧化物阴离子自由基(O2·–)的产生能够磁响应扩增,在500 mT时分别实现66.9%和28.0%的最大产率提高。
在各种癌症细胞模型中,这种磁增强的氧自由基产生表现出比传统PDT方案普遍的细胞毒性优势。值得注意的是,小鼠乳腺癌4T1细胞的半抑制浓度(IC50)在常氧和缺氧条件下均显著降低,在常氧条件下观察到最明显的降低,从0.91μM(单独PDT)降至0.38μM(磁PDT)。磁增强的治疗效果显著抑制了原位肿瘤的生长。这种磁PDT范式建立了一种在生物应用中操纵自旋依赖性光敏化过程的新策略。
附:英文原文
Title: Spin Manipulation Engineering of Photodynamic Intermediates: Magnetic Amplification of Oxyradicals Generation for Enhanced Antitumor Phototherapeutic Efficacy
Author: Jiuyu Lu, Junying Ding, Zhuoran Xia, Zhuo Yang, Chengyuan Lv, Shenglin Zong, Jianfang Cao, Danhong Zhou, Saran Long, Wen Sun, Jianjun Du, Jiangli Fan, Xiaojun Peng
Issue&Volume: May 13, 2025
Abstract: Improving the photosensitization efficiency represents a critical challenge in photodynamic therapy (PDT) research. While cyanines exhibit potential as photosensitizers (PSs) due to their large extinction coefficients and excellent biocompatibility, the inherent limitations in intersystem crossing severely affect therapeutic efficacy. Herein, we proposed a bottom-up magnetically enhanced photodynamic therapy (magneto-PDT) paradigm employing fluorobenzene-substituted pentamethine cyanine as type-I reactive oxygen species generators. Based on the radical pair mechanism and magnetic field effect, the notable difference in g-factors (Δg) between PSs and oxyradicals enabled magnetically responsive amplification of Cy5–3,4,5–3F-mediated hydroxyl radical (OH) and superoxide anion radical (O2–) production, achieving maximum yield enhancements of 66.9 and 28.0% respectively at 500 mT. This magnetically augmented oxyradicals generation exhibited universal cytotoxicity superiority over conventional PDT protocols in various cancer cell models. Notably, the semi-inhibitory concentration (IC50) of murine mammary carcinoma 4T1 cells demonstrated a remarkable reduction under both normoxic and hypoxic conditions, with the most pronounced decrease observed in normoxia from 0.91 μM (PDT alone) to 0.38 μM (magneto-PDT). The significantly magneto-enhanced therapeutic performance effectively inhibited orthotopic tumor growth. This magneto-PDT paradigm established a novel strategy for manipulating spin-dependent photosensitization processes in biological applications.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c04111
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c04111
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
