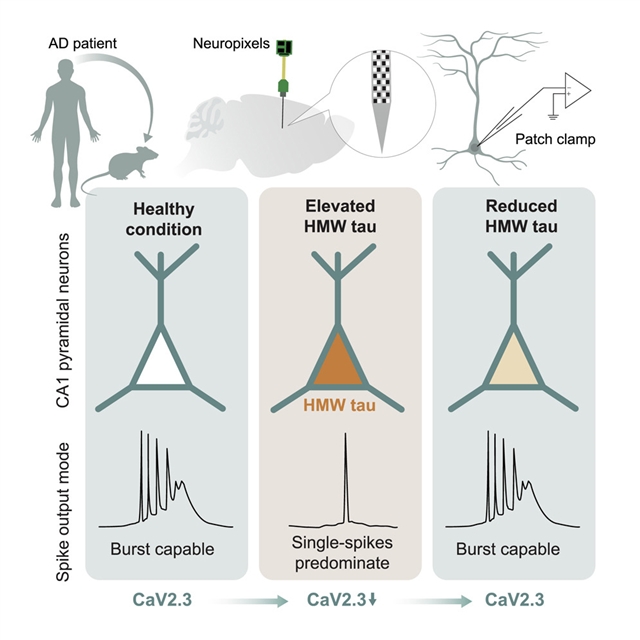
近日,英国伦敦大学学院英国痴呆症研究所教授Marc Aurel Busche及其研究团队揭示了阿尔茨海默病患者来源的高分子量tau损伤海马神经元破裂。相关论文于2025年4月28日发表于国际顶尖学术期刊《细胞》杂志上。
该课题组人员在小鼠模型中使用了活体神经像素和膜片钳记录,并证明tau独立于β-淀粉样蛋白,选择性地削弱CA1海马神经元的复杂spike爆发放电,这是支持学习和记忆的基本细胞机制。破裂受损与海马网络活动的改变有关,海马网络活动与破裂放电模式(即θ节律和高频波纹)相关联,并且与CaV2.3钙通道的神经元表达减少同时发生,而CaV2.3钙通道对于体内的破裂放电至关重要。随后,小组从人类AD大脑中分离出可溶性高分子量(HMW) tau,作为负责抑制突发放电的tau物种。这些数据提供了AD中tau依赖性认知能力下降的细胞机制,并暗示了一种罕见的细胞内HMW tau作为治疗靶点。
研究人员表示,Tau蛋白积累与阿尔茨海默病(AD)的认知症状密切相关。然而,记忆认知的tau依赖性衰退的细胞驱动因素仍然是未知的。
附:英文原文
Title: Alzheimer’s disease patient-derived high-molecular-weight tau impairs bursting in hippocampal neurons
Author: Samuel S. Harris, Robert Ellingford, Jana Hartmann, Debanjan Dasgupta, Marten Kehring, Rikesh M. Rajani, David Graykowski, Noé Quittot, Dhanush Sivasankaran, Caitlin Commins, Zhanyun Fan, Suraya A. Bond, Fred Wolf, David Dupret, Raymond J. Dolan, Arthur Konnerth, Andreas Neef, Bradley T. Hyman, Marc Aurel Busche
Issue&Volume: 2025-04-28
Abstract: Tau accumulation is closely related to cognitive symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, the cellular drivers of tau-dependent decline of memory-based cognition remain elusive. Here, we employed in vivo Neuropixels and patch-clamp recordings in mouse models and demonstrate that tau, independent of β-amyloid, selectively debilitates complex-spike burst firing of CA1 hippocampal neurons, a fundamental cellular mechanism underpinning learning and memory. Impaired bursting was associated with altered hippocampal network activities that are coupled to burst firing patterns (i.e., theta rhythms and high-frequency ripples) and was concurrent with reduced neuronal expression of CaV2.3 calcium channels, which are essential for burst firing in vivo. We subsequently identify soluble high molecular weight (HMW) tau, isolated from human AD brain, as the tau species responsible for suppression of burst firing. These data provide a cellular mechanism for tau-dependent cognitive decline in AD and implicate a rare species of intracellular HMW tau as a therapeutic target.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.04.006
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell/abstract/S0092-8674(25)00408-8
