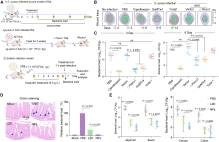
2025年4月21日,中国农业大学朱奎小组在《细胞》杂志发表论文,报道了组织几何形状在时空上驱动细菌感染。
研究组展示了以生物工程策略为主题的上皮组织中细菌的几何引导感染模式。研究小组发现,细胞牵引力通过触发机械敏感离子通道蛋白Piezo1与细菌的共定位,在上皮单层细菌侵袭部位和边缘感染模式的调节中起着至关重要的作用。此外,该课题组开发了精确的基于机械生物学的策略来增强伤口和肠道感染动物模型的抗菌效果。他们的研究结果表明,组织几何对介导细菌的时空感染具有关键影响,这对发现和开发对抗细菌感染的替代策略具有重要意义。
据了解,上皮组织是抵抗细菌感染的第一道防线。上皮组织的自组织不断适应微环境的结构和机制,从而动态地影响感染的初始生态位。然而,组织几何形状调节细菌感染的机制仍然知之甚少。
附:英文原文
Title: Tissue geometry spatiotemporally drives bacterial infections
Author: Yiming Han, Xiaoye Liu, Shaoqi Qu, Xiaocen Duan, Yunqing Xiang, Nan Jiang, Shuyu Yang, Xu Fang, Liang Xu, Hui Wen, Yue Yu, Shuqiang Huang, Jianyong Huang, Kui Zhu
Issue&Volume: 2025-04-21
Abstract: Epithelial tissues serve as the first line of host against bacterial infections. The self-organization of epithelial tissues continuously adapts to the architecture and mechanics of microenvironments, thereby dynamically impacting the initial niche of infections. However, the mechanism by which tissue geometry regulates bacterial infection remains poorly understood. Here, we showed geometry-guided infection patterns of bacteria in epithelial tissues using bioengineering strategies. We discovered that cellular traction forces play a crucial role in the regulation of bacterial invasive sites and marginal infection patterns in epithelial monolayers through triggering co-localization of mechanosensitive ion channel protein Piezo1 with bacteria. Further, we developed precise mechanobiology-based strategies to potentiate the antibacterial efficacy in animal models of wound and intestinal infection. Our findings demonstrate that tissue geometry exerts a key impact on mediating spatiotemporal infections of bacteria, which has important implications for the discovery and development of alternative strategies against bacterial infections.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.03.042
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell/abstract/S0092-8674(25)00394-0
