哈尔滨医科大学杨宝峰研究组在研究中取得进展。他们报道了KLX通过介导ZBP1的转录和泛素化以及增加ZBP1诱导的PANoptosis来改善肝癌。2025年3月27日,国际知名学术期刊《中国药理学报》发表了这一成果。
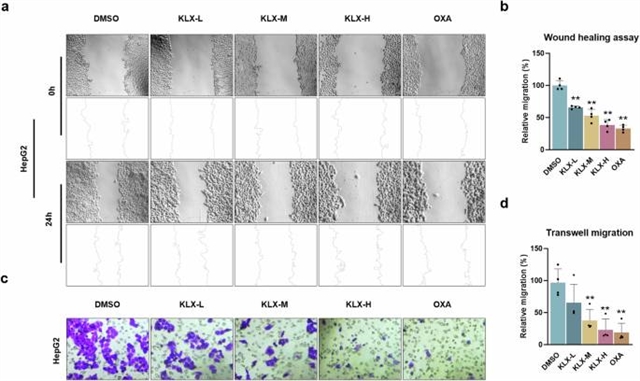
在这项研究中,该研究组评估了一种新的蒽醌衍生物康乐新(KLX)治疗肝癌的潜力。在体外,KLX以剂量依赖性的方式抑制HepG2和Hep3B细胞的增殖和迁移。在机制上,KLX上调Z-DNA结合蛋白1 (ZBP1)的表达,通过直接结合ZBP1,改变其构象,降低其对E3泛素连接酶环指蛋白180 (RNF180)的亲和力,诱导PANoptosis。这种相互作用降低了ZBP1的泛素化,从而增加了它的稳定性。此外,KLX上调转录因子同源盒D10 (HOXD10)的表达,进一步增加ZBP1的表达。ZBP1水平升高可显著抑制肝癌细胞的增殖和迁移,而KLX的抑制作用在ZBP1下调后被逆转。在异种移植模型中,KLX显著抑制肿瘤生长,毒性低于奥沙利铂(OXA)。综上所述,KLX通过上调ZBP1并阻止其降解,促进肝癌细胞PANoptosis,从而抑制肝癌的进展和迁移。这些发现表明KLX是一种很有前景的肝癌治疗剂。
据悉,肝癌是一种高度侵袭性的恶性肿瘤,生存率很低。目前的治疗方法,包括肝移植、免疫治疗和基因治疗,往往受到晚期诊断和显著副作用的限制,因此迫切需要新的治疗药物。
附:英文原文
Title: KLX ameliorates liver cancer progression by mediating ZBP1 transcription and ubiquitination and increasing ZBP1-induced PANoptosis
Author: Wang, Zhuo, Yang, Yang, Yao, Fang-ting, Zhang, Feng, Lin, Ke-ying, Diao, Hong-tao, Zhao, Qiao-yue, Kong, Xue, Si, Wei, Xie, Ya-ting, Song, Jing-lun, Zeng, Ling-hua, Wang, Chun-lei, Xiong, Yu-ting, Zou, Kun-kun, Wang, Xiao-man, Zhang, Xin-yue, Wu, Han, Jiang, Wei-tao, Bian, Yu, Yang, Bao-feng
Issue&Volume: 2025-03-27
Abstract: Liver cancer is a highly aggressive malignancy with poor survival rates. Current treatments, including liver transplantation, immunotherapy, and gene therapy, are often limited by late-stage diagnosis and significant side effects, highlighting the urgent need for novel therapeutic agents. In this study, we evaluated the therapeutic potential of Kanglexin (KLX), a novel anthraquinone derivative, in the treatment of liver cancer. In vitro, KLX inhibited the proliferation and migration of HepG2 and Hep3B cells in a dose-dependent manner. Mechanistically, KLX upregulated Z-DNA binding protein 1 (ZBP1) expression, inducing PANoptosis by directly binding to ZBP1, altering its conformation, and reducing its affinity for the E3 ubiquitin ligase ring finger protein 180 (RNF180). This interaction decreased ZBP1 ubiquitination, thereby increasing its stability. Additionally, KLX upregulated the expression of the transcription factor homeobox D10 (HOXD10), which further increased ZBP1 expression. Elevated ZBP1 levels significantly suppressed liver cancer cell proliferation and migration, whereas the inhibitory effects of KLX were reversed upon ZBP1 knockdown. In a xenograft model, KLX significantly inhibited tumor growth with a lower toxicity than oxaliplatin (OXA). In conclusion, KLX promoted PANoptosis in liver cancer cells by upregulating ZBP1 and preventing its degradation, thereby inhibiting liver cancer progression and migration. These findings suggest that KLX is a promising therapeutic agent for liver cancer.
DOI: 10.1038/s41401-025-01528-4
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41401-025-01528-4
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica:《中国药理学报》,创刊于1980年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:8.2
官方网址:http://www.chinaphar.com/
投稿链接:https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/aphs
