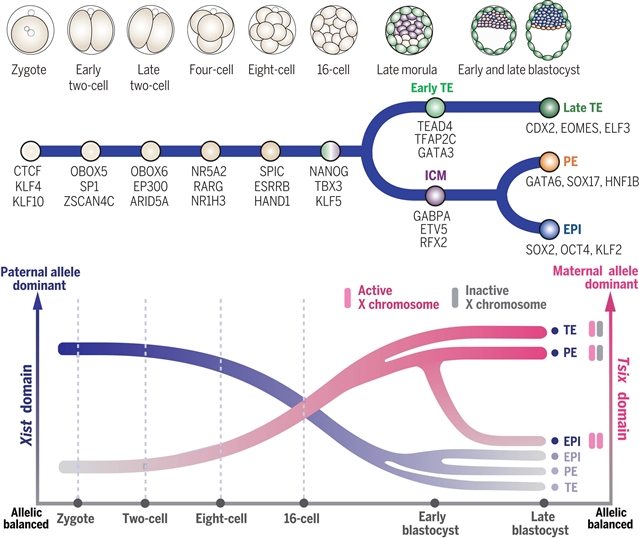
课题组开发了scNanoATAC-seq2,这是一种用于转座酶可及的染色质主题化长读测序的单细胞检测方法。该研究组展示了多主题着床前发育的染色质可及性景观,揭示了在谱系分离过程中外胚层、原始内胚层和滋养外胚层中不同的染色质特征。合子和双细胞胚胎之间的差异突出了在母体到合子过渡期间染色质可及性的重编程。单细胞长读测序能够深入分析非典型印迹、印迹X染色体失活和低映射性基因组区域(如重复元件和相似物)的染色质可及性。他们的数据为哺乳动物着床前发育和谱系分化过程中的染色质动力学提供了见解。
据介绍,在哺乳动物中,受精卵经历全基因组的表观遗传重编程以产生生物体。然而,他们对胚胎着床前发育过程中单细胞分辨率的表观遗传动力学的理解仍然不完整。
附:英文原文
Title: Chromatin accessibility landscape of mouse early embryos revealed by single-cell NanoATAC-seq2
Author: Mengyao Li, Zhenhuan Jiang, Xueqiang Xu, Xinglong Wu, Yun Liu, Kexuan Chen, Yuhan Liao, Wen Li, Xiao Wang, Yuqing Guo, Bo Zhang, Lu Wen, Kehkooi Kee, Fuchou Tang
Issue&Volume: 2025-03-28
Abstract: In mammals, fertilized eggs undergo genome-wide epigenetic reprogramming to generate the organism. However, our understanding of epigenetic dynamics during preimplantation development at single-cell resolution remains incomplete. Here, we developed scNanoATAC-seq2, a single-cell assay for transposase-accessible chromatin using long-read sequencing for scarce samples. We present a detailed chromatin accessibility landscape of mouse preimplantation development, revealing distinct chromatin signatures in the epiblast, primitive endoderm, and trophectoderm during lineage segregation. Differences between zygotes and two-cell embryos highlight reprogramming in chromatin accessibility during the maternal-to-zygotic transition. Single-cell long-read sequencing enables in-depth analysis of chromatin accessibility in noncanonical imprinting, imprinted X chromosome inactivation, and low-mappability genomic regions, such as repetitive elements and paralogs. Our data provide insights into chromatin dynamics during mammalian preimplantation development and lineage differentiation.
DOI: adp4319
Source: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adp4319
