安徽医科大学王华课题组在研究中取得进展。他们的最新研究揭示了E1A刺激基因1的肝细胞抑制因子通过促进自噬来保护对乙酰氨基酚诱导的肝损伤。这一研究成果于2025年3月25日发表在国际顶尖学术期刊《中国药理学报》上。
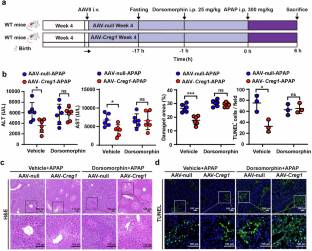
在这项研究中,小组探讨了CREG1在AILI中的作用和治疗潜力。课题组研究人员发现,在AILI小鼠和药物性肝损伤(DILI)患者的肝脏中,CREG1的表达水平显著升高,在对乙酰氨基酚(APAP)处理的原代肝细胞中也观察到这一点。与Creg1fl/fl小鼠相比,肝细胞特异性CREG1缺乏小鼠对APAP更敏感,而AAV8介导的CREG1过表达可保护小鼠免受AILI。该团队证明了CREG1缺乏会损害自噬并激活炎症信号通路。预给药A769662激活AMPK或雷帕霉素诱导自噬可预防Creg1Δhep小鼠肝损伤。同时,CREG1过表达对AILI的保护作用可被AMPK抑制剂dorsomorphin抑制。这些发现表明,CREG1通过AMPK激活调节自噬来缓解AILI, CREG1代表了一个有希望的AILI治疗靶点。
据了解,对乙酰氨基酚诱导的肝损伤(AILI)在急性肝衰竭中占很大比例,这强调了阐明AILI发病机制和确定有效治疗药物的迫切需要。E1A刺激基因1的细胞抑制因子(CREG1)是一种分泌糖蛋白,在维持肝脏稳态中起着至关重要的作用。先前的研究表明,CREG1可减轻与多种肝脏疾病相关的肝损伤、脂肪变性和炎症。
附:英文原文
Title: Hepatocyte cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes 1 protects against acetaminophen-induced liver injury by promoting autophagy
Author: Cheng, Qian-ying, Wu, Miao-miao, Wei, Xiao-li, Lu, Li-li, Liu, Run-dong, Li, Yuan-hao, Zhu, Ni-na, Li, Ya-qun, Zuo, Li, Wang, Hua
Issue&Volume: 2025-03-25
Abstract: Acetaminophen-induced liver injury (AILI) accounts for a significant proportion of acute liver failure emphasizing the critical need to elucidate AILI pathogenesis and to identify effective therapeutic agents. Cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes 1 (CREG1) is a secreted glycoprotein that plays a crucial role in maintaining liver homeostasis. Prior studies have shown that CREG1 mitigates liver injury, steatosis, and inflammation associated with multiple liver diseases. In this study we investigated the role and therapeutic potential of CREG1 in AILI. We showed that the expression levels of CREG1 were markedly elevated in livers of AILI mice and patients with drug-induced liver injury (DILI), which was also observed in primary hepatocytes treated with acetaminophen (APAP). Hepatocyte-specific CREG1 deficiency mice were more sensitive to APAP compared to Creg1fl/fl mice, whereas AAV8-mediated CREG1 overexpression protected mice from AILI. We demonstrated that CREG1 deficiency impaired autophagy and activated inflammatory signaling pathways. Pre-administration of A769662 to activate AMPK or rapamycin to induce autophagy prevented the liver injury in Creg1Δhep mice. Coherently, the protective effect of CREG1 overexpression against AILI could be inhibited by dorsomorphin, an AMPK inhibitor. These findings suggest that CREG1 alleviates AILI by regulating autophagy through AMPK activation, and CREG1 represents a promising therapeutics target for AILI treatment.
DOI: 10.1038/s41401-025-01532-8
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41401-025-01532-8
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica:《中国药理学报》,创刊于1980年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:8.2
官方网址:http://www.chinaphar.com/
投稿链接:https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/aphs
