一种针对真菌细胞膜磷脂的多烯大环内酯,这一成果由中国药科大学王宗强小组经过不懈努力而取得。该项研究成果发表在2025年3月19日出版的《自然》上。
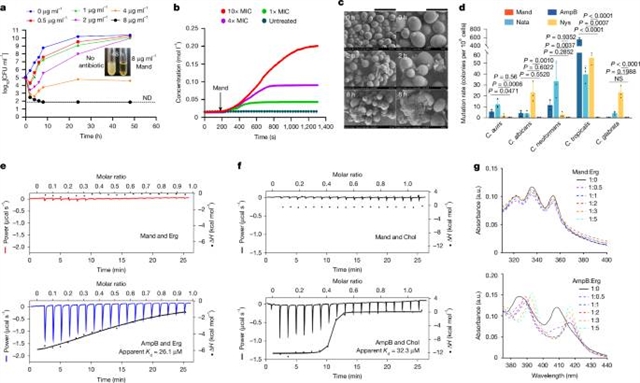
在这里,研究组报告了一种多烯抗真菌抗生素,下颌骨霉素的发现,主题是一个系统发育引导的天然产物发现平台。下颌骨霉素是由mand基因克隆器生物合成的,从已知的多烯大环内酯类抗生素以不同的方式进化而来,并用三个脱氧糖修饰。在体外和体内环境中,它已显示出对多种多重耐药真菌病原体的有效和广谱杀真菌活性。与已知的以麦角甾醇为靶点的多烯大环内酯类抗生素不同,下颌骨霉素具有独特的作用模式,可靶向真菌细胞膜中的各种磷脂,从而从真菌细胞中释放必需离子。这种结合多个靶标的独特能力使其具有强大的杀真菌活性以及逃避耐药性的能力。以系统发育为导向的天然产物发现策略为主题的下颌骨霉素的鉴定代表了发现具有不同作用模式的抗菌化合物的重要进展,可以开发用于对抗多药耐药真菌病原体。
研究人员表示,耐多药致病真菌的全球传播对人类健康构成严重威胁,因此有必要发现具有独特作用模式的抗真菌药物。然而,传统的基于活性的筛选先前未描述的抗生素受到高频重新发现已知化合物和缺乏新的抗真菌靶点的阻碍。
附:英文原文
Title: A polyene macrolide targeting phospholipids in the fungal cell membrane
Author: Deng, Qisen, Li, Yinchuan, He, Wenyan, Chen, Tao, Liu, Nan, Ma, Lingman, Qiu, Zhixia, Shang, Zhuo, Wang, Zongqiang
Issue&Volume: 2025-03-19
Abstract: The global spread of multidrug-resistant pathogenic fungi presents a serious threat to human health, necessitating the discovery of antifungals with unique modes of action1. However, conventional activity-based screening for previously undescribed antibiotics has been hampered by the high-frequency rediscovery of known compounds and the lack of new antifungal targets2. Here we report the discovery of a polyene antifungal antibiotic, mandimycin, using a phylogeny-guided natural-product discovery platform. Mandimycin is biosynthesized by the mand gene cluster, has evolved in a distinct manner from known polyene macrolide antibiotics and is modified with three deoxy sugars. It has demonstrated potent and broad-spectrum fungicidal activity against a wide range of multidrug-resistant fungal pathogens in both in vitro and in vivo settings. In contrast to known polyene macrolide antibiotics that target ergosterol, mandimycin has a unique mode of action that involves targeting various phospholipids in fungal cell membranes, resulting in the release of essential ions from fungal cells. This unique ability to bind multiple targets gives it robust fungicidal activity as well as the capability to evade resistance. The identification of mandimycin using the phylogeny-guided natural-product discovery strategy represents an important advancement in uncovering antimicrobial compounds with distinct modes of action, which could be developed to combat multidrug-resistant fungal pathogens.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08678-9
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-08678-9
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
