天津医科大学于春水团队的一项最新研究提出了杏仁核和亚核体积的跨祖先和性别分层全基因组关联分析。该项研究成果发表在2025年3月17日出版的《自然—遗传学》上。
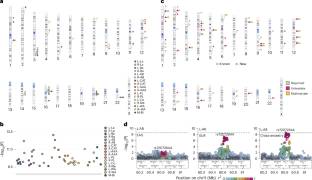
在这里,研究组对6923名中国人和48634名欧洲人的21个杏仁核体积性状进行了跨祖先和性别分层的全基因组关联分析。该研究组发现了191个变异性状关联(P< 2.38 × 10-9),其中性别组合单变量分析中有47个新关联(12个新基因座),性别组合和性别分层多变量分析中有7个新基因座。研究人员确定了12种特定于祖先和2种特定于性别的关联。鉴定的遗传变异包括16个精细定位的因果变异,并调节杏仁核和胎儿大脑的基因表达。这些变异丰富了大脑发育,并与情绪、认知和神经精神疾病共定位。这些结果表明,跨祖先和性别分层的遗传关联分析可能有助于了解杏仁核和亚核体积的遗传结构。
据了解,杏仁核是一个小而重要的多核结构,对情绪、认知和神经精神疾病起着至关重要的作用。尽管在性别组合的欧洲人群中研究了与杏仁核体积性状的遗传关联,但缺乏跨祖先和性别分层分析。
附:英文原文
Title: Cross-ancestry and sex-stratified genome-wide association analyses of amygdala and subnucleus volumes
Author: Ji, Yuan, Liu, Nana, Yang, Yunjun, Wang, Meiyun, Cheng, Jingliang, Zhu, Wenzhen, Qiu, Shijun, Geng, Zuojun, Cui, Guangbin, Yu, Yongqiang, Liao, Weihua, Zhang, Hui, Gao, Bo, Xu, Xiaojun, Han, Tong, Yao, Zhenwei, Zhang, Quan, Qin, Wen, Liu, Feng, Liang, Meng, Wang, Sijia, Xu, Qiang, Xu, Jiayuan, Fu, Jilian, Zhang, Peng, Li, Wei, Shi, Dapeng, Wang, Caihong, Lui, Su, Yan, Zhihan, Chen, Feng, Zhang, Jing, Shen, Wen, Miao, Yanwei, Wang, Dawei, Gao, Jia-Hong, Zhang, Xiaochu, Xu, Kai, Zuo, Xi-Nian, Zhang, Longjiang, Ye, Zhaoxiang, Li, Mulin Jun, Xian, Junfang, Zhang, Bing, Yu, Chunshui
Issue&Volume: 2025-03-17
Abstract: The amygdala is a small but critical multi-nucleus structure for emotion, cognition and neuropsychiatric disorders. Although genetic associations with amygdala volumetric traits have been investigated in sex-combined European populations, cross-ancestry and sex-stratified analyses are lacking. Here we conducted cross-ancestry and sex-stratified genome-wide association analyses for 21 amygdala volumetric traits in 6,923 Chinese and 48,634 European individuals. We identified 191 variant–trait associations (P<2.38×10-9), including 47 new associations (12 new loci) in sex-combined univariate analyses and seven additional new loci in sex-combined and sex-stratified multivariate analyses. We identified 12 ancestry-specific and two sex-specific associations. The identified genetic variants include 16 fine-mapped causal variants and regulate amygdala and fetal brain gene expression. The variants were enriched for brain development and colocalized with mood, cognition and neuropsychiatric disorders. These results indicate that cross-ancestry and sex-stratified genetic association analyses may provide insight into the genetic architectures of amygdala and subnucleus volumes.
DOI: 10.1038/s41588-025-02136-y
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-025-02136-y
Nature Genetics:《自然—遗传学》,创刊于1992年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:41.307
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/ng/
投稿链接:https://mts-ng.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
