美国麻省理工学院Alfredo Alexander-Katz研究组揭示了设计单聚合物链纳米颗粒模拟生物分子水合挫折。2025年3月12日出版的《自然-化学》发表了这项成果。
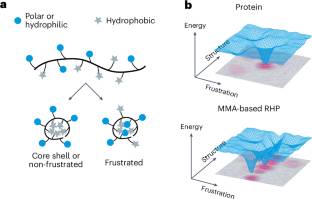
在这里,该课题组人员发现由随机杂多聚合物组成的单链纳米颗粒可以显示出相似的水合反应水平。该课题组研究人员将这些纳米颗粒分为三种类型,基于是否疏水或亲水性残基,或两者都显示出热态。课题组提出了一系列的物理化学规则来决定这些纳米粒子的状态。该课题组研究人员在具有不同骨架和残基的单聚合物链纳米粒子的原子和简化蒙特卡罗模型中证明了这些规则的普遍性。他们的工作为单链纳米颗粒的设计提供了见解,单链纳米颗粒是一种新兴的聚合物形态,它实现了制造具有生物蛋白质功能的聚合物材料的简单性和成本。
据了解,天然折叠蛋白依赖于雕刻其活性或结合位点的局部化学环境,以及它们的形状,以实现功能。特别是,蛋白质通过水合作用——控制亲水残基的脱水和疏水残基的水合作用——来增强它们的化学或结合活性。
附:英文原文
Title: Designing single-polymer-chain nanoparticles to mimic biomolecular hydration frustration
Author: Jin, Tianyi, Coley, Connor W., Alexander-Katz, Alfredo
Issue&Volume: 2025-03-12
Abstract: Native folded proteins rely on sculpting the local chemical environment of their active or binding sites, as well as their shapes, to achieve functionality. In particular, proteins use hydration frustration—control over the dehydration of hydrophilic residues and the hydration of hydrophobic residues—to amplify their chemical or binding activity. Here we uncover that single-polymer-chain nanoparticles formed by random heteropolymers comprising four or more components can display similar levels of hydration frustration. We categorize these nanoparticles into three types based on whether either hydrophobic or hydrophilic residues, or both types, display frustrated states. We propose a series of physicochemical rules that determine the state of these nanoparticles. We demonstrate the generality of these rules in atomistic and simplified Monte Carlo models of single-polymer-chain nanoparticles with different backbones and residues. Our work provides insights into the design of single-chain nanoparticles, an emerging polymer modality that achieves the ease and cost of fabrication of polymeric material with the functionality of biological proteins.
DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-01760-9
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-025-01760-9
Nature Chemistry:《自然—化学》,创刊于2009年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:24.274
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nchem/
投稿链接:https://mts-nchem.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
