中国科学院生态环境研究中心李伟峰研究团队报道了基于深度学习的GluN1/GluN3A受体抑制剂筛选策略。该项研究成果发表在2025年3月11日出版的《中国药理学报》上。
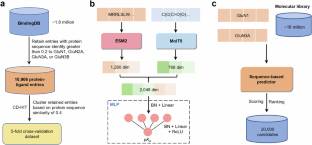
为了解决这一问题,课题组研究人员设计了一种基于深度学习的策略,以平衡识别GluN1/GluN3A抑制剂的效率和准确性。首先,开发了基于序列的评分功能,以快速筛选包含1800万个化合物的文库,将候选库减少到大约105个。接下来,使用两个基于复杂评分函数IGModel和RTMScore对剩余候选人进行精确评分和排名。最后得到IC50为2.87±0.80的活性分子。通过全细胞电压箝位电生理证实了GluN1/GluN3A受体的μM。本研究还提出了一种将深度学习整合到快速、精确的高通量筛选中的范例。
据悉,GluN1/GluN3A受体是最近在中枢神经系统中发现的一种独特的兴奋性甘氨酸受体,它挑战了n -甲基- d -天冬氨酸(NMDA)受体多样性和甘氨酸能信号传导的传统观点。它在情绪调节中的作用使其成为神经精神疾病的潜在治疗靶点。然而,GluN1/GluN3A受体的药理研究仍处于早期阶段。传统的离子通道药物发现的高通量筛选方法往往缺乏效率,特别是当应用于大型化合物文库时。
附:英文原文
Title: An efficient deep learning-based strategy to screen inhibitors for GluN1/GluN3A receptor
Author: Wang, Ze-chen, Zeng, Yue, Sun, Jin-yuan, Chen, Xue-qin, Wu, Hao-chen, Li, Yang-yang, Mu, Yu-guang, Zheng, Liang-zhen, Gao, Zhao-bing, Li, Wei-feng
Issue&Volume: 2025-03-11
Abstract: The GluN1/GluN3A receptor, a unique excitatory glycine receptor recently identified in the central nervous system, challenges traditional perspectives of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor diversity and glycinergic signaling. Its role in emotional regulation positions it as a potential therapeutic target for neuropsychiatric disorders. However, pharmacological research on GluN1/GluN3A receptors remains at an early stage. Traditional high-throughput screening methods for ion channel drug discovery often lack efficiency, particularly when applied to large compound libraries. To address this concern, we designed a deep learning-based strategy that balances efficiency and accuracy for identifying GluN1/GluN3A inhibitors. First, a sequence-based scoring function was developed to rapidly screen a library containing 18 million compounds, reducing the pool to approximately 105 candidates. Next, two complex-based scoring functions, IGModel and RTMScore, were employed to precisely score and rank the remaining candidates. Finally, an active molecule with an IC50 of 2.87±0.80μM for the GluN1/GluN3A receptor was confirmed through whole-cell voltage-clamp electrophysiology. This study also presents a paradigm for integrating deep learning into rapid and precise high-throughput screening.
DOI: 10.1038/s41401-025-01513-x
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41401-025-01513-x
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica:《中国药理学报》,创刊于1980年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:8.2
官方网址:http://www.chinaphar.com/
投稿链接:https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/aphs
