山东大学郭秀丽研究组在研究中取得进展。他们揭示了CYP2A6通过抑制SRC/Wnt/β-Catenin通路抑制肝癌。该项研究成果发表在2025年3月11日出版的《中国药理学报》上。
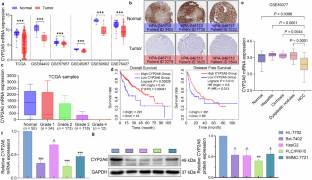
在这项研究中,该研究团队研究了细胞色素P-450 2A6 (CYP2A6)在HCC进展中的作用,聚焦于其作为诊断生物标志物和治疗靶点的潜力。通过分析TCGA和GEO数据库,课题组人员发现CYP2A6在HCC中的表达水平明显低于正常组织。CYP2A6过表达导致PLC/PRF/5和HepG2细胞体外增殖、迁移、侵袭、粘附、成管,以及裸鼠的致瘤性和转移性降低。值得注意的是,CYP2A6的抗HCC作用独立于其代谢功能。课题组证明CYP2A6可以结合原癌基因酪氨酸蛋白激酶SRC (SRC)并抑制SRC/Wnt/β-Catenin通路。SRC过表达消除了上调CYP2A6对PLC/PRF/5细胞迁移和侵袭的抑制作用。这些结果共同表明CYP2A6作为HCC的生物标志物和治疗靶点的潜力。它对SRC/Wnt/β-Catenin通路的调节为HCC治疗提供了新的见解。
研究人员表示,晚期肝细胞癌(HCC)患者面临有限的治疗选择,迫切需要更有效的早期检测方法和先进的治疗模式。新的证据表明,多种CYP450蛋白参与HCC的发病机制。CYP1A2、CYP2E1和CYP3A5调节重要的信号通路,从而抑制HCC细胞的增殖和侵袭。
附:英文原文
Title: CYP2A6 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma via inhibiting SRC/Wnt/β-Catenin pathway
Author: Liu, Yi-fan, Feng, Li-ya, Zhang, Wan-ying, Zhang, Xu, Shao, Li-jun, Zhao, Xiao-man, Ji, Jian-bo, Guo, Xiu-li
Issue&Volume: 2025-03-11
Abstract: Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) at advanced stages face limited treatment options, highlighting the urgent need for more effective early detection methods and advanced therapeutic modalities. Emerging evidence shows that multiple CYP450 proteins are involved in the pathogenesis of HCC. CYP1A2, CYP2E1 and CYP3A5 have been shown to modulate important signaling pathways, hereby inhibiting the proliferation and invasion of HCC cells. In this study we investigated the role of cytochrome P-450 2A6 (CYP2A6) in HCC progression, focusing on its potential as a diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target. By analyzing TCGA and GEO databases, we found that the expression levels of CYP2A6 were significantly decreased in HCC compared to normal tissues. Overexpression of CYP2A6 resulted in reduced proliferation, migration, invasion, adhesion, tube-forming in PLC/PRF/5 and HepG2 cells in vitro, as well as tumorigenicity and metastasis in nude mice. Notably, the anti-HCC effects of CYP2A6 were independent of its metabolic functions. We demonstrated that CYP2A6 could bind to proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase SRC (SRC) and inhibit the SRC/Wnt/β-Catenin pathway. Overexpression of SRC abrogated the inhibitory effects of upregulating CYP2A6 on the migration and invasion of PLC/PRF/5 cells. These results together suggest the potential of CYP2A6 as a biomarker and therapeutic target for HCC. Its modulation of the SRC/Wnt/β-Catenin pathway provides a new insight for HCC treatment.
DOI: 10.1038/s41401-025-01524-8
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41401-025-01524-8
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica:《中国药理学报》,创刊于1980年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:8.2
官方网址:http://www.chinaphar.com/
投稿链接:https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/aphs
