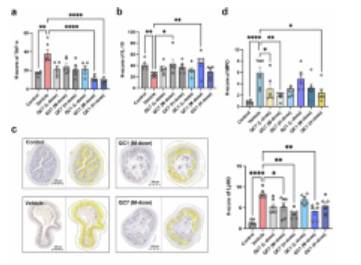
复旦大学李智平研究组取得一项新突破。他们揭示了口服FPR2/ALX调节剂调节骨髓细胞活性,改善炎症性肠病的粘膜炎症。这一研究成果发表在2025年3月11日出版的国际学术期刊《Acta Pharmacologica Sinica》上。
在这项研究中,研究小组评估了两种小分子FPR2/ALX调节剂(激动剂Quin-C1和拮抗剂Quin-C7)对IBD的治疗效果。该课题组人员首先分析了Quin-C1-FPR2与异三聚体Gi配合物的低温电镜结构,揭示了配体识别和FPR2激活的结构基础。然后,该课题组人员建立了正常小鼠和髓系衰竭小鼠的葡聚糖硫酸钠(DSS)诱导的结肠炎模型。研究人员发现,口服Quin-C1 7天可以改善dss诱导的结肠炎,这可以通过减轻疾病活动性指数、降低结肠组织病理学评分和纠正细胞因子紊乱来证明。同时,研究组发现口服FPR2/ALX拮抗剂Quin-C7具有与Quin-C1相似的治疗作用。在症状改善方面,Quin-C1和Quin-C7的ED50值为1.3660Mg /kg和2.2110毫克/公斤。潜在的机制涉及ERK-或ERK/ jnk介导的髓细胞调节,限制了结肠炎和炎症的发展。这是首次证明由合成小分子FPR2/ALX调节剂主导的抗结肠炎特性,这意味着FPR2/ALX调节剂而不是单独的激动剂可以改善IBD。
据悉,目前炎症性肠病(IBD)的治疗很大程度上依赖于抗炎和免疫抑制策略,其疗效和不良事件令人难以接受。目前尚没有治疗IBD的解决或修复药物,但甲酰基肽受体2 (FPR2/ALX)等潜在靶点可能填补这一空白。
附:英文原文
Title: Oral FPR2/ALX modulators tune myeloid cell activity to ameliorate mucosal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease
Author: Yang, Wen-sheng, Liu, Qing, Li, Yang, Li, Guan-yi, Lin, Shi, Li, Jie, Li, Lin-yu, Li, Yuan, Ge, Xi-lin, Wang, Xiao-zhen, Wu, Wei, Yan, Jun, Wang, Guang-fei, Zhou, Qing-tong, Liu, Qiang, Wang, Ming-Wei, Li, Zhi-ping
Issue&Volume: 2025-03-11
Abstract: Current treatments of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) largely depend on anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive strategies with unacceptable efficacy and adverse events. Resolution or repair agents to treat IBD are not available but potential targets like formyl peptide receptor 2 (FPR2/ALX) may fill the gap. In this study we evaluated the therapeutic effects of two small molecule FPR2/ALX modulators (agonist Quin-C1 and antagonist Quin-C7) against IBD. We first analyzed the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the Quin-C1–FPR2 in complex with heterotrimeric Gi to reveal the structural basis for ligand recognition and FPR2 activation. We then established dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis model in both normal and myeloid depletion mice. We showed that oral administration of Quin-C1 for 7 days ameliorated DSS-induced colitis evidenced by alleviated disease activity indexes, reduced colonic histopathological scores, and corrected cytokine disorders. Meanwhile, we found that oral administration of FPR2/ALX antagonist Quin-C7 exerted therapeutic actions similar to those of Quin-C1. In terms of symptomatic improvements, the ED50 values of Quin-C1 and Quin-C7 were 1.3660mg/kg and 2.2110mg/kg, respectively. The underlying mechanisms involved ERK- or ERK/JNK-mediated myeloid cell regulation that limited the development of colitis and inflammation. This is the first demonstration of anti-colitis property caused by synthetic small molecule FPR2/ALX modulators, implying that FPR2/ALX modulation rather than agonism alone ameliorates IBD.
DOI: 10.1038/s41401-025-01525-7
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41401-025-01525-7
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica:《中国药理学报》,创刊于1980年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:8.2
官方网址:http://www.chinaphar.com/
投稿链接:https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/aphs
