首都医科大学赵国光小组在研究中取得进展。他们揭示了神经炎症和网络异常在耐药癫痫中的作用。相关论文于2025年2月24日发表在《神经科学通报》杂志上。
该课题组人员从多个角度关注神经炎症和脑网络异常在DRE中的作用,以确定临床应用的关键点。小组希望提供一个有见地的概述,以推动寻求更好的DRE治疗。
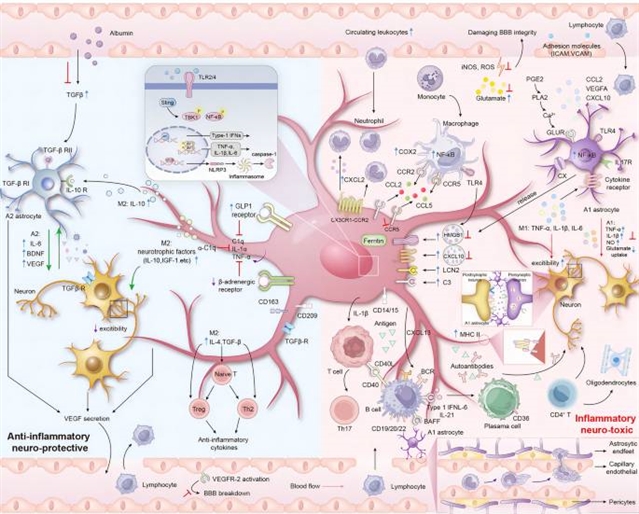
据了解,全世界有5000多万人患有癫痫。耐药癫痫(DRE)占这些病例的三分之一,神经炎症被认为在这些病例中起作用。尽管在DRE领域是一个长期争论的问题,但神经炎症的机制尚未得到充分阐明。通过单细胞多模态转录组学研究了DRE患者脑组织中的促炎微环境。有证据表明,神经系统中的炎症细胞和促炎细胞因子可导致广泛的生化变化,如连接蛋白半通道兴奋性和神经递质稳态的破坏。炎症的存在可能引起神经网络异常,从而抑制内源性抗癫痫系统。
附:英文原文
Title: The Role of Neuroinflammation and Network Anomalies in Drug-Resistant Epilepsy
Author: Shi, Jianwei, Xie, Jing, Li, Zesheng, He, Xiaosong, Wei, Penghu, Sander, Josemir W, Zhao, Guoguang
Issue&Volume: 2025-02-24
Abstract: Epilepsy affects over 50 million people worldwide. Drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE) accounts for up to a third of these cases, and neuro-inflammation is thought to play a role in such cases. Despite being a long-debated issue in the field of DRE, the mechanisms underlying neuroinflammation have yet to be fully elucidated. The pro-inflammatory microenvironment within the brain tissue of people with DRE has been probed using single-cell multimodal transcriptomics. Evidence suggests that inflammatory cells and pro-inflammatory cytokines in the nervous system can lead to extensive biochemical changes, such as connexin hemichannel excitability and disruption of neurotransmitter homeostasis. The presence of inflammation may give rise to neuronal network abnormalities that suppress endogenous antiepileptic systems. We focus on the role of neuroinflammation and brain network anomalies in DRE from multiple perspectives to identify critical points for clinical application. We hope to provide an insightful overview to advance the quest for better DRE treatments.
DOI: 10.1007/s12264-025-01348-w
Source: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12264-025-01348-w
Neuroscience Bulletin:《神经科学通报》,创刊于2006年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:5.6
官方网址:https://link.springer.com/journal/12264
投稿链接:https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/nsb
