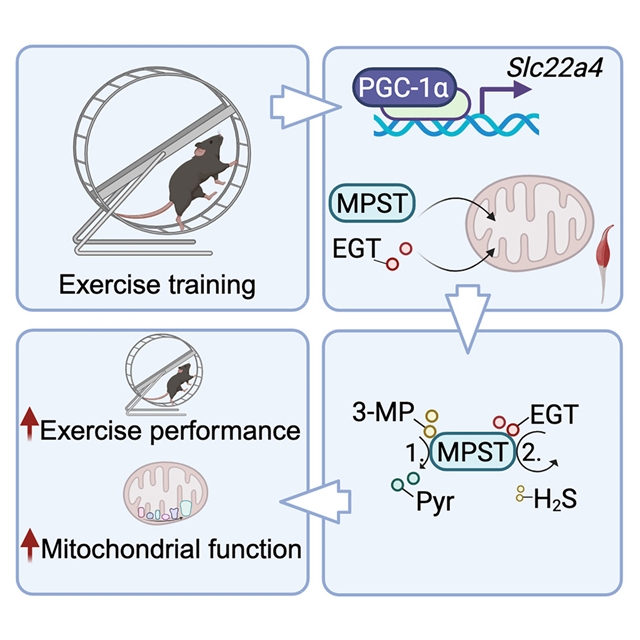
美国丹娜-法伯癌症研究所Bruce M. Spiegelman小组近日取得一项新成果,他们发现麦角硫因通过直接激活MPST来控制线粒体功能和运动表现。相关论文于2025年2月17日发表于国际顶尖学术期刊《细胞—代谢》杂志上。
该研究团队采用了一种系统的方法来确定线粒体如何重塑其代谢组以响应运动训练。从这些数据中,课题组发现EGT在运动训练后在线粒体中积累。蛋白质组热稳定性研究确定3-巯基丙酮酸硫转移酶(MPST)是EGT的直接分子靶点;EGT结合并激活MPST,从而促进小鼠线粒体呼吸和运动训练表现。总之,这些数据确定了第一个生理学上相关的EGT靶点,并建立了EGT-MPST轴作为调节线粒体功能和运动表现的分子机制。
据介绍,麦角硫因(EGT)是一种来源于饮食的非典型氨基酸,在人体组织中积累到高水平。EGT水平降低与年龄相关的疾病有关,包括神经退行性疾病和心血管疾病,而EGT补充在广泛的疾病和衰老模型中具有保护作用。尽管有这些有希望的数据,EGT的直接和生理相关的分子靶点仍然是未知的。
附:英文原文
Title: Ergothioneine controls mitochondrial function and exercise performance via direct activation of MPST
Author: Hans-Georg Sprenger, Melanie J. Mittenbühler, Yizhi Sun, Jonathan G. Van Vranken, Sebastian Schindler, Abhilash Jayaraj, Sumeet A. Khetarpal, Amanda L. Smythers, Ariana Vargas-Castillo, Anna M. Puszynska, Jessica B. Spinelli, Andrea Armani, Tenzin Kunchok, Birgitta Ryback, Hyuk-Soo Seo, Kijun Song, Luke Sebastian, Coby O’Young, Chelsea Braithwaite, Sirano Dhe-Paganon, Nils Burger, Evanna L. Mills, Steven P. Gygi, Joao A. Paulo, Haribabu Arthanari, Edward T. Chouchani, David M. Sabatini, Bruce M. Spiegelman
Issue&Volume: 2025-02-17
Abstract: Ergothioneine (EGT) is a diet-derived, atypical amino acid that accumulates to high levels in human tissues. Reduced EGT levels have been linked to age-related disorders, including neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases, while EGT supplementation is protective in a broad range of disease and aging models. Despite these promising data, the direct and physiologically relevant molecular target of EGT has remained elusive. Here, we use a systematic approach to identify how mitochondria remodel their metabolome in response to exercise training. From these data, we find that EGT accumulates in muscle mitochondria upon exercise training. Proteome-wide thermal stability studies identify 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (MPST) as a direct molecular target of EGT; EGT binds to and activates MPST, thereby boosting mitochondrial respiration and exercise training performance in mice. Together, these data identify the first physiologically relevant EGT target and establish the EGT-MPST axis as a molecular mechanism for regulating mitochondrial function and exercise performance.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2025.01.024
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(25)00024-5
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
