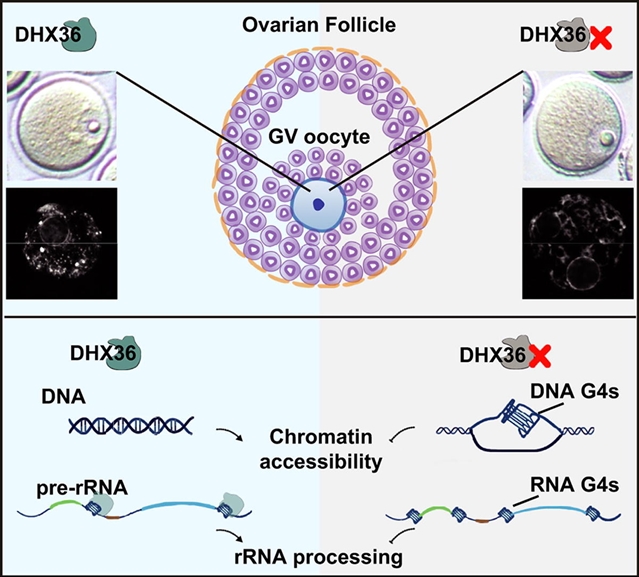
值得注意的是,该研究团队在生长的GV卵母细胞中观察到rRNA转录不足,在完全生长的GV卵母细胞中也观察到pre-rRNA加工和翻译活性不足。使用G4探针和抗体,课题组人员发现CKO GV卵母细胞染色质和细胞质中G4s的形成增加,主要来源于rDNA和pre-rRNA。
DHX36的分布与pre-rRNA和G4s的分布在时空上是同步的。体外实验证实DHX36通过RHAU-特异性基序(RSM)直接与pre-rRNA结合。过表达DHX36可部分缓解成熟CKO卵母细胞中pre-rRNA的积累。总之,本研究强调了DHX36在维持雌性生殖能力中的生理意义,强调了其在单核母细胞中通过G4解绕机制参与rRNA稳态和染色质配置的关键作用。
据悉,DHX36通过与G-四重复合物(G4s)的相互作用,在调控转录和转录后过程中起着至关重要的作用。DHX36调节G4s的机制在不同的细胞类型和生理条件下存在差异。利用卵母细胞特异性条件敲除(CKO)小鼠,研究DHX36缺乏对雌性生殖能力的影响。结果显示,CKO小鼠表现出严重的激素反应、排卵和完全不育。CKO生发囊泡(GV)卵母细胞表现为核仁大,染色质结构异常,染色质可及性降低,转录组紊乱,减数分裂进程受到抑制。受精后,CKO卵母细胞停留在受精卵或2细胞期。
附:英文原文
Title: DHX36-mediated G-quadruplexes unwinding is essential for oocyte and early embryo development in mice
Author: Heng-Yu Fan a b d
Issue&Volume: 2025/02/17
Abstract: DHX36 plays a crucial role in regulating transcriptional and post-transcriptional processes through its interaction with G-quadruplexes (G4s). The mechanisms by which DHX36 regulates G4s vary across different cell types and physiological conditions. Oocyte-specific conditional knockout (CKO) mice were utilized to study the impact of DHX36 deficiency on female fertility. The results show that the CKO mice exhibit severely impaired hormone response, ovulation, and complete infertility. The CKO germinal vesicle (GV) oocytes display large nucleoli, aberrant chromatin configuration, decreased chromatin accessibility, disturbed transcriptome, and inhibited meiosis progression. Following fertilization, the CKO oocytes arrest at the zygote or 2-cell stage. Notably, we observed inadequate rRNA transcription in growing GV oocytes, as well as insufficient pre-rRNA processing and translation activity in fully-grown GV oocytes. Using a G4 probe and antibody, we found increased G4s formation at the chromatin and cytoplasm of CKO GV oocytes, which mainly originate from the rDNA and pre-rRNA. Furthermore, the distribution of DHX36 was found to be spatiotemporally synchronized with that of pre-rRNA and G4s in early mouse embryos. In vitro experiments confirmed that DHX36 directly binds with pre-rRNA through the RHAU-specific motif (RSM). Overexpression of DHX36 could partially alleviate the pre-rRNA accumulation in fully-grown CKO oocytes. In conclusion, this study highlights the physiological significance of DHX36 in maintaining female fertility, underscoring its critical role in rRNA homeostasis and chromatin configuration through G4-unwinding mechanism in mouse oocytes.
DOI: 10.1016/j.scib.2025.02.017
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2095927325001793
Science Bulletin:《科学通报》,创刊于1950年。隶属于SciEngine出版平台,最新IF:18.9
官方网址:https://www.sciengine.com/SB/home
投稿链接:https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/csb
