2025年2月11日出版的《美国化学会杂志》发表了科学家的一项最新研究成果。来自
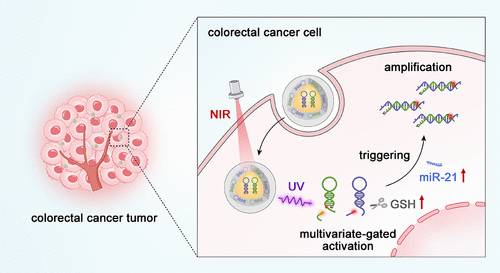
该研究组报道了一种多变量门控催化发夹组装(CHA)纳米传感器,用于人类结直肠癌组织中microRNA-21 (miR-21)的特异性放大成像,以揭示miR-21相关的潜在分子机制。内源性谷胱甘肽和外源性近红外多变量门控设计结合CHA探针提高了靶miR-21的信号强度,减少了背景干扰。纳米传感器能够在体内对miR-21进行特异性放大成像,与传统CHA方法相比,信本比是1.6倍。利用所设计的纳米传感器,研究组实现了临床手术切除标本中肿瘤组织和正常组织的初步识别。研究发现,过表达的miR-21可抑制参与DNA损伤识别和修复的核心错配修复识别蛋白human mutS homologue 2,从而抑制结直肠癌的治疗效果。该探针设计策略将多变量门控激活方法与信号放大系统相结合,适用于miRNA精确成像和疾病相关分子机制研究。
研究人员表示,MicroRNA (miRNA)参与结直肠癌的发生和发展。miRNA在肿瘤部位的体内成像对于了解其在结直肠癌病理和治疗靶点鉴定中的作用至关重要。然而,肿瘤细胞中miRNA的低丰度和正常组织中的非特异性信号泄漏阻碍了对肿瘤部位miRNA的准确成像。
附:英文原文
Title: Spatially Selective MicroRNA Imaging in Human Colorectal Cancer Tissues Using a Multivariate-Gated Signal Amplification Nanosensor
Author: Xiaoming Zhang, Wenhui Chen, Songlin Wan, Bing Qu, Fei Liao, Di Cheng, Yun Zhang, Zhao Ding, Yanbing Yang, Quan Yuan
Issue&Volume: February 11, 2025
Abstract: MicroRNA (miRNA) is involved in the genesis in viand development of colorectal cancer. The in vivo imaging of miRNA at the tumor sites is essential for understanding its role in colorectal cancer pathology and therapeutic target identification. However, achieving accurate imaging of miRNA at the tumor sites is hindered by the low abundance of miRNAs in tumor cells and nonspecific signal leakage in normal tissues. Here, we report a multivariate-gated catalytic hairpin assembly (CHA) nanosensor for the specific amplified imaging of microRNA-21 (miR-21) in human colorectal cancer tissues to reveal the underlying miR-21-associated molecular mechanism. The endogenous glutathione and exogenous near-infrared multivariate-gated design in combination with CHA probes improves the signal strength of target miR-21 and reduces the background interference. The nanosensor enables specific amplified imaging of miR-21 in vivo, and the signal-to-background ratios are 1.6-fold compared with traditional CHA methods. With the assistance of the designed nanosensor, we achieve the preliminary identification of tumor tissues and normal tissues from human clinical surgical resection samples. The overexpressed miR-21 is found to suppress the core mismatch repair recognition protein human mutS homologue 2 involved in DNA damage recognition and repair to inhibit the therapeutic efficacy of colorectal cancer. The strategy of probe design, which combines multivariate-gated activation methods with a signal amplification system, is applicable for accurate miRNA imaging and disease-relevant molecular mechanism research.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c16001
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.4c16001
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
