上海理工大学顾敏小组的最新研究探明了拓扑驱动的能量转移网络上转换受激发射耗尽显微镜。2025年12月4日,国际知名学术期刊《光:科学与应用》发表了这一成果。
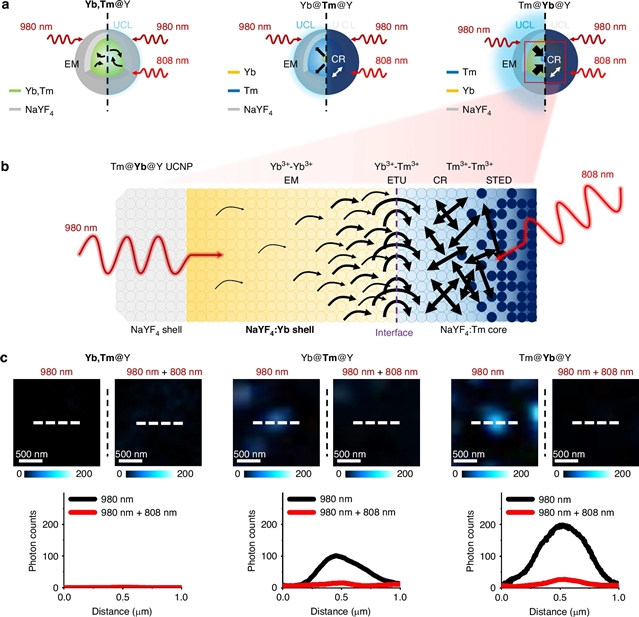
该课题组人员在镧掺杂上转换纳米颗粒中引入拓扑驱动的能量转移网络,用于降低激光强度的上转换受激发射耗尽显微镜,保持高光子预算。50nm核壳纳米颗粒中Yb3+敏化剂和Tm3+发射体的空间分离增强了超分辨显微镜的能量传递动力学。拓扑相关的能量迁移在低功率980纳米激发下产生强大的450纳米上转换发光。增强的交叉弛豫提高了光开关效率,在980纳米激发和808纳米损耗条件下实现了0.06 MW cm-2的饱和强度。采用高斯分布的980纳米激发激光(0.03 MW cm-2)和环形分布的808纳米损耗激光(1 MW cm-2),实现了65纳米横向分辨率的超分辨率成像,与传统方法相比,激发强度降低10倍,损耗强度降低3倍。这些发现证明了利用上转换纳米颗粒中拓扑相关的能量传递动力学来推进低功耗超分辨率应用的潜力。
据介绍,镧系掺杂上转换纳米粒子使上转换受激发射耗尽显微镜具有高光稳定性和低强度近红外连续波激光器。控制这些纳米颗粒中的能量传递动力学对于具有最小激光强度和高光子预算的超分辨率显微镜至关重要。然而,传统方法忽略了镧系离子的空间分布及其对能量传递动力学的影响。
附:英文原文
Title: Topology-driven energy transfer networks for upconversion stimulated emission depletion microscopy
Author: Gu, Weizhao, Lamon, Simone, Yu, Haoyi, Zhang, Qiming, Gu, Min
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-04
Abstract: Lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles enable upconversion stimulated emission depletion microscopy with high photostability and low-intensity near-infrared continuous-wave lasers. Controlling energy transfer dynamics in these nanoparticles is crucial for super-resolution microscopy with minimal laser intensities and high photon budgets. However, traditional methods neglect the spatial distribution of lanthanide ions and its effect on energy transfer dynamics. Here, we introduce topology-driven energy transfer networks in lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles for upconversion stimulated emission depletion microscopy with reduced laser intensities, maintaining a high photon budget. Spatial separation of Yb3+ sensitizers and Tm3+ emitters in 50-nm core-shell nanoparticles enhance energy transfer dynamics for super-resolution microscopy. Topology-dependent energy migration produces strong 450-nm upconversion luminescence under low-power 980-nm excitation. Enhanced cross-relaxation improves optical switching efficiency, achieving a saturation intensity of 0.06MWcm2 under excitation at 980nm and depletion at 808nm. Super-resolution imaging with a 65-nm lateral resolution is achieved using intensities of 0.03MWcm2 for a Gaussian-shaped excitation laser at 980nm and 1MWcm2 for a donut-shaped depletion laser at 808nm, representing a 10-fold reduction in excitation intensity and a 3-fold reduction in depletion intensity compared to conventional methods. These findings demonstrate the potential of harnessing topology-dependent energy transfer dynamics in upconversion nanoparticles for advancing low-power super-resolution applications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-02054-y
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-02054-y
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
