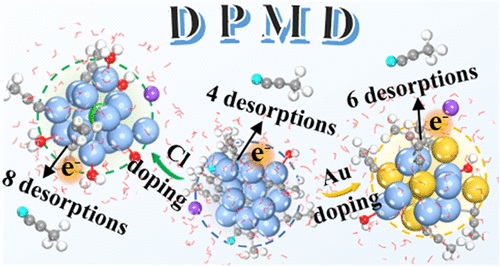
结合多尺度恒电位模拟和深电位分子动力学(DPMD)方案,该研究团队在深度学习框架内建立了一个高精度的机器学习力场,以阐明全炔基保护的Ag15 NC及其掺杂体系(Ag8Au7、Ag9Cu6和Ag14Cl NC)的电化学结构演变。该课题组人员发现所有nc的金属核都经历了从八面体到无序的转变,伴随着表面炔基配体的部分或完全裂解。掺杂剂通过调节解吸途径来调节稳定性,Ag9Cu6 NC表现出优异的抗解离性,这是由于Cu-C键的紧密结合。他们基于训练好的机器学习力场的纳秒级DPMD模拟进一步证实,掺杂显著影响了解吸炔配体的数量(Ag15为4个,Ag8Au7为6个,Ag14Cl为8个)和核心有序程度,并且长期模拟>2000 ps对于捕获动态电化学界面至关重要。该研究首次建立了电化学界面动力学与掺杂效应之间的定量关联,为设计高稳定的原子精密催化剂提供了理论范式。
据介绍,由炔基配体保护的原子级精密银纳米(NCs)是一类新兴的电催化剂,在CO2电还原等反应中表现出高活性和选择性。然而,在电化学操作条件下,它们的动态结构演化机制尚不清楚。传统的实验表征面临着解决原子尺度动态过程的巨大挑战,而从头算分子动力学(AIMD)模拟仅局限于皮秒时间尺度,不足以捕捉更长时间内的进化动力学。
附:英文原文
Title: Capturing Dynamic Core Reconstruction and Ligand Desorption of Atomically Precise Ag Nanoclusters with Machine Learning Force Field
Author: Fang Sun, Qing Tang
Issue&Volume: December 4, 2025
Abstract: Atomically precise silver nanoclusters (NCs) protected by alkynyl ligands represent an emerging class of electrocatalysts demonstrating high activity and selectivity in reactions, such as CO2 electroreduction. However, their dynamic structural evolution mechanisms under electrochemical operating conditions remain elusive. Conventional experimental characterization faces a grand challenge to resolve atomic-scale dynamic processes, while ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) simulations are solely confined to picosecond time scales, insufficient for capturing the dynamics of evolution over longer times. Combining multiscale constant potential simulations and a deep potential molecular dynamics (DPMD) scheme, here we developed a high-accuracy machine learning force field within the deep-learning framework to elucidate the electrochemical structural evolution in all-alkynyl-protected Ag15 NC and its doped systems (Ag8Au7, Ag9Cu6, and Ag14Cl NCs). We found that the metal cores of all NCs undergo a transition from octahedral to disordered, accompanied by partial or complete cleavage of surface alkynyl ligands. The dopants critically modulate the stability by regulating desorption pathways, with Ag9Cu6 NC exhibiting exceptional resistance to dissociation due to robust Cu–C bonding. Our nanosecond-level DPMD simulations based on trained machine learning force fields further confirmed that doping dramatically affects the number of desorbed alkyne ligands (4 for Ag15, 6 for Ag8Au7, and 8 for Ag14Cl) and the degree of core ordering, and a long-term simulation of >2000 ps was crucial for capturing the dynamic electrochemical interface. This study established the first quantitative correlation between electrochemical interface dynamics and doping effects, providing a theoretical paradigm for designing highly stable atomically precise catalysts.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c15207
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c15207
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
