南方医科大学李亮小组的最新研究探明了尿苷耗竭损害CD8+ T细胞通过N-糖基化抗肿瘤活性。2025年12月29日出版的《细胞—代谢》杂志发表了这项成果。
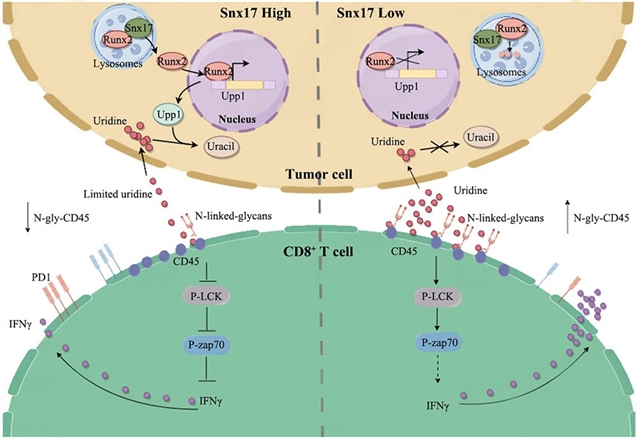
免疫检查点阻断(ICB)由于成本高、疗效有限而面临局限性。本研究确定SNX17是ICB抗性的关键媒介。在人和小鼠中,SNX17的升高与抗PD-1反应较差相关。肿瘤细胞中SNX17缺失通过CD8+ T细胞依赖机制抑制肿瘤生长。SNX17降低肿瘤微环境(TME)中的尿苷,抑制IFN-γ并上调CD8+ T细胞中的PD1。外源性尿苷在低snx17肿瘤中显示出与抗PD-1/PD-L1相当的抗肿瘤疗效,并克服了高snx17模型的耐药。尿苷通过促进CD45 N -糖基化和LCK磷酸化增强CD8+ T细胞功能。机制上,SNX17稳定RUNX2,促进TME中UPP1的转录和尿苷的降解。这些发现将SNX17定位为ICB反应生物标志物,并提名尿苷作为一种具有成本效益的免疫治疗策略。
附:英文原文
Title: Uridine depletion impairs CD8+ T cell antitumor activity through N-glycosylation
Author: Jianbiao Xiao, Zhiyang Li, Yi Ding, Kejin Zhu, Zhihao Zheng, Yaowei Zhang, Jiawen Weng, Feifei Wang, Yuqin Zhang, Sisi Zeng, Minxing Qiu, Zhaowen Zhang, Zhizhang Wang, Li Liang
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-29
Abstract: Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) faces limitations owing to high cost and restricted efficacy. This study identifies SNX17 as a key mediator of ICB resistance. Elevated SNX17 correlates with poor anti-PD-1 response in humans and mice. SNX17 deletion in tumor cells inhibits tumor growth via CD8+ T cell-dependent mechanisms. SNX17 reduces uridine in the tumor microenvironment (TME), suppressing IFN-γ and upregulating PD1 in CD8+ T cells. Exogenous uridine shows antitumor efficacy comparable to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 in low-SNX17 tumors and overcomes resistance in high-SNX17 models. Uridine enhances CD8+ T cell function by promoting CD45 N-glycosylation and LCK phosphorylation. Mechanistically, SNX17 stabilizes RUNX2, promoting UPP1 transcription and uridine degradation in the TME. These findings position SNX17 as an ICB response biomarker and nominate uridine as a cost-effective immunotherapeutic strategy.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2025.11.016
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(25)00530-3
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
