近日,吉林大学姚向东团队研究了质子交换膜电催化水分解用超耐用酸性氧化钌析氧催化剂。相关论文于2025年12月23日发表在《美国化学会志》上。
二氧化钌(RuO2)因其高活性和相对较低的成本,成为质子交换膜水电解槽(PEMWEs)极具前景的候选材料。然而,其有限的稳定性仍是关键挑战。尽管已有大量研究致力于提升其稳定性,但现有进展仍难以满足实际PEMWEs的需求。
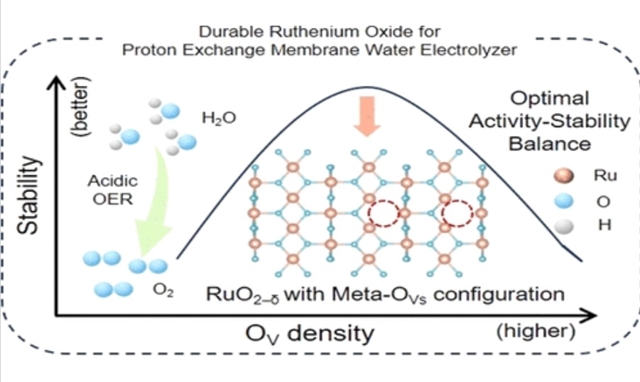
研究组通过精确调控RuO2−δ的本征结构——特别是氧空位(OVs),定量探究其活性-稳定性平衡的内在规律。结合理论计算与实验结果,研究发现由氧空位密度控制的氧空位间空间距离主导着催化性能,例如:活性随空位间距减小呈指数衰减,而稳定性则呈现类高斯函数波动。电化学分析表明,所合成的氧空位密度为33%的h-RuO2−δ纳米片实现了最佳的活性-稳定性协同,在PEMWE中展现出卓越的活性(1 A cm–2@1.63 V)与稳定性(超过120小时),性能远超商业RuO2催化剂。
原位傅里叶变换红外光谱与密度泛函理论计算证实,具有最佳氧空位空间排布(元氧空位构型)的RuO2−δ能够削弱界面水的氢键网络,促进水分子解离,并在析氧反应过程中表现出增强的结构稳定性。该研究结果为钌基催化剂的缺陷工程建立了定量的构效关系。
附:英文原文
Title: Super Durable Acidic Oxygen Evolution Catalyst of Ruthenium Oxide for Proton Exchange Membrane Electrocatalytic Water Splitting
Author: Dongdong Zhang, Qilong Wu, Yun Han, Liyun Wu, Hongliang Dong, Rongrong Zhang, Nan Song, Fangfang Zhu, Yiqing Fang, Haodong Liu, Jun Chen, Aijun Du, KeKe Huang, Pei Yuan, Xiangdong Yao
Issue&Volume: December 23, 2025
Abstract: Ruthenium oxide (RuO2) is a promising candidate for proton exchange membrane water electrolyzers (PEMWEs) due to its high activity and relatively low cost. However, its limited stability remains a critical challenge. Although substantial efforts have been made to improve the stability, the advance is insufficient for requirement of practical PEMWEs. In this study, the intrinsic structure of RuO2δ, specifically oxygen vacancies (OVs), was precisely manipulated to quantitatively investigate the underlying principles governing its activity–stability balance. Combining theoretical calculations and experimental results, it is revealed that the spatial distance between OVs controlled by the density of OV dictates the catalytic performance, e. g. activity decays exponentially as intervacancy distance decreases while stability exhibits Gaussian-like fluctuations. Electrochemical analysis demonstrates that the as-synthesized h-RuO2δ nanosheet, with an OV density of 33%, achieves an optimal activity–stability synergy, exhibiting exceptional activity (1 A cm–2@1.63 V) and stability (over 120 h) in a PEMWE, far surpassing the performance of commercial RuO2 catalyst. In situ FTIR and DFT calculations demonstrate that RuO2δ with an optimal spatial arrangement of OVs (Meta-OVs configuration) weakens the hydrogen-bonding network of interfacial water, facilitating water dissociation, and exhibits enhanced structural stability during the oxygen evolution reaction. The findings of this study establish a quantitative structure–property relationship for defect engineering in Ru-based catalysts.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c16939
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c16939
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
