南方医科大学李博团队近日取得一项新成果。经过不懈努力,他们的最新研究揭示了线粒体VHL在缺氧条件下重塑细胞代谢。相关论文于2025年12月22日发表在《细胞—代谢》杂志上。
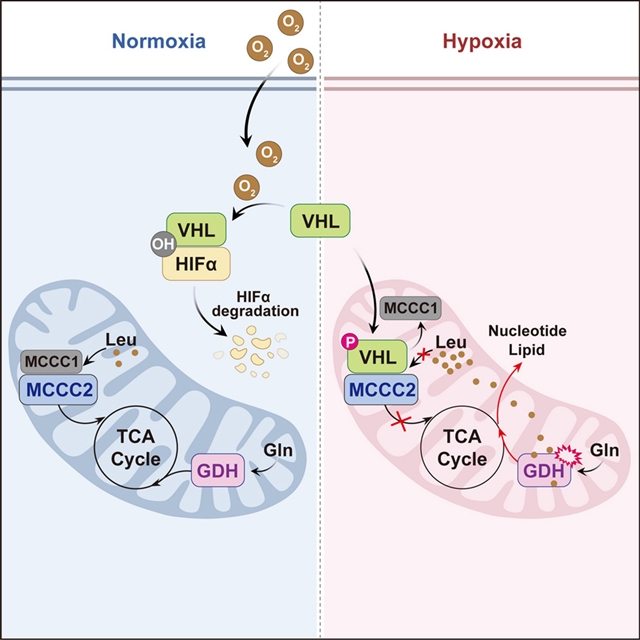
该研究团队发现大多数细胞质VHL在慢性缺氧下被降解,剩余的VHL池主要转移到线粒体。线粒体VHL结合并抑制3-甲基丁基辅酶A羧化酶亚基2 (MCCC2),这是亮氨酸分解代谢机制的重要亚基。积累的亮氨酸变构激活谷氨酸脱氢酶,促进谷氨酰胺水解,产生足够的脂质和核苷酸,以支持缺氧细胞的生长。
此外,SRC介导的VHL磷酸化和蛋白精氨酸甲基转移酶5 (PRMT5)介导的MCCC2甲基化协同调节VHL-MCCC2相互作用和伴随的代谢变化,这在缺血性损伤动物模型中得到了概括,并在功能上与癌症中的VHL突变相关。他们的研究强调了VHL是线粒体内缺氧代谢的真正调节器,而不是缺氧条件下HIFs的唯一“备用适配器”。
据悉,在正常缺氧条件下,von Hippel-Lindau (VHL)蛋白靶向缺氧诱导因子(HIFs)的氧诱导羟基化α亚基降解,以协调哺乳动物的氧感应。然而,当蛋白羟基化作用减弱时,VHL是否在缺氧中起非规范作用仍不清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: Mitochondrial VHL rewires cell metabolism in hypoxia
Author: Guobang Li, Wenfeng Pan, Long Wu, Zhiliang Cai, Haoming Chen, Xingui Wu, Tiantian Yu, Kun Liao, Hui Zhang, Xingqiao Wen, Bo Li
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-22
Abstract: Under normoxia, von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) protein targets the oxygen-induced, hydroxylated α subunits of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) for degradation to orchestrate mammalian oxygen sensing. However, whether VHL plays non-canonical roles in hypoxia, when protein hydroxylation is attenuated, remains elusive. Here, we show that most cytosolic VHL is degraded under chronic hypoxia, with the remaining VHL pool primarily translocating to the mitochondria. Mitochondrial VHL binds and inhibits 3-methylcrotonyl-coenzyme A carboxylase subunit 2 (MCCC2), an essential subunit of the leucine catabolic machinery. Accumulated leucine allosterically activates glutamate dehydrogenase to promote glutaminolysis, generating sufficient lipids and nucleotides to support hypoxic cell growth. Furthermore, SRC-mediated VHL phosphorylation and protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5)-mediated MCCC2 methylation synergistically regulate the VHL-MCCC2 interaction and concomitant metabolic changes, which are recapitulated in animal models of ischemic injury and functionally associated with VHL mutations in cancer. Our study highlights VHL as a bona fide regulator of hypoxic metabolism within mitochondria, rather than a solely “standby adaptor” for HIFs under hypoxia.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2025.11.013
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(25)00527-3
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
