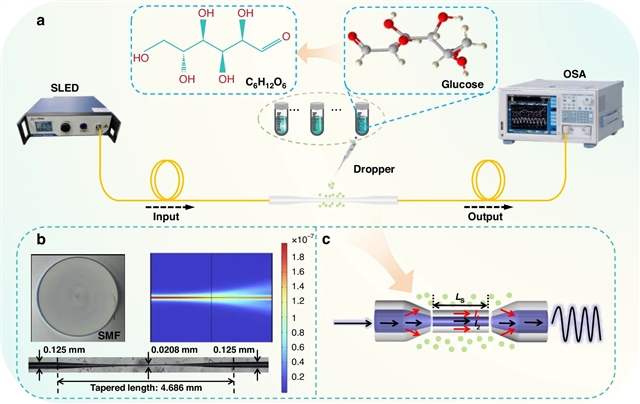
清华大学杨四刚与燕山大学陈海良课题组的一项最新研究揭示了LSTM辅助光纤干涉传感:突破自由光谱范围的限制。这一研究成果发表在2025年12月1日出版的国际学术期刊《光:科学与应用》上。
光纤干涉传感器以其高灵敏度和高质量的特性在化学、生物、医学等领域具有重要的应用价值。
然而,由于自由光谱范围的限制,宽测量范围和高灵敏度之间的权衡是干扰传感器发展的长期挑战,从根本上阻碍了其在精密测量应用中的广泛应用。在这项工作中,利用长短期记忆神经网络在基于马赫-曾德尔干涉的折射率传感器中打破了自由光谱范围的限制。长短期记忆神经网络独特的门控机制使其能够有效地处理长期依赖的序列信息,如干扰谱,避免了对复杂频谱信号的分析。干涉光谱与折射率之间建立了一一对应关系,均方根误差为3.029 × 10-4,决定系数为0.99971。在不牺牲灵敏度的情况下,测量范围从1.3333-1.3561的单一自由光谱范围扩展到1.3333-1.3921的大约三个自由光谱范围。
此外,有足够的训练数据可以实现更大的测量范围。该工作成功地解决了光干涉传感器高灵敏度和宽动态测量范围的固有矛盾,为下一代智能传感系统开辟了道路。
附:英文原文
Title: LSTM-assisted optical fiber interferometric sensing: breaking the limitation of free spectral range
Author: Hu, Junling, Zhang, Sa, Cai, Meiyu, Ma, Mingjian, Li, Shuguang, Chen, Hailiang, Yang, Sigang
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-01
Abstract: Optical fiber interferometric sensors are of great importance in chemistry, biology, and medicine disciplines owing to high-sensitivity and high-quality factor. However, due to the limitation of free spectral range, the inherent trade-off between wide measurement range and high sensitivity poses a persistent challenge in interference sensor development, which has fundamentally hindered their widespread adoption in precision measurement applications. In this work, a long short-term memory neural network is utilized in a Mach-Zehnder interference-based refractive index sensor to break the free spectral range limitation. Unique gating mechanism in long short-term memory neural network enables it to efficiently process long-term dependent sequence information, such as interference spectrum, avoiding the need for complex spectral signal analysis. A one-to-one mapping relationship is established between the interference spectrum and refractive index with root mean square error of 3.029×104 and a coefficient of determination of 0.99971. The measurement range is extended from a single free spectral range of 1.3333–1.3561 to approximately three free spectral ranges of 1.3333–1.3921 without sacrificing sensitivity. Moreover, a wider measurement range can be achieved with sufficient training data. This work successfully resolves the inherent contradiction between high sensitivity and wide dynamic measurement range in optical interference-based sensors, opening up a path for the next generation of intelligent sensing systems.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-02008-4
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-02008-4
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
