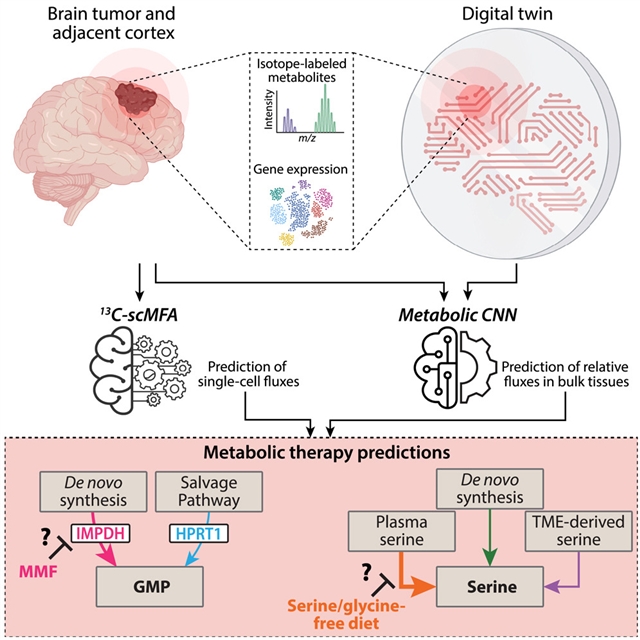
美国密歇根大学Deepak Nagrath小组的研究开发出了数字双胞胎用于脑癌患者体内代谢通量估计。相关论文于2025年12月1日发表在《细胞—代谢》杂志上。
为了解决这些限制并实现人类患者的通量估计,课题组人员开发了两个基于机器学习的框架。首先,数字孪生框架(DTF)将第一性原理化学计量学和同位素模拟与卷积神经网络相结合,以估计患者大量样品中的通量。其次,单细胞代谢通量分析(13C-scMFA)框架将患者单细胞RNA测序(scRNA-seq)数据与13c同位素示踪相结合,允许单细胞水平的通量量化。
这些研究可以量化肿瘤胶质瘤细胞的代谢活性,揭示与非恶性细胞相比,嘌呤合成和丝氨酸摄取经常升高。他们的模型还确定了脑癌患者和小鼠的代谢异质性,进而预测对代谢抑制剂的治疗反应。他们的框架推进了体内代谢通量分析,可能导致新的代谢疗法,并为患者的代谢导向疗法确定生物标志物。
据介绍,体内代谢通量估计的最新进展仅限于临床前模型,主要是由于组织采样,肿瘤微环境(TME)异质性和非稳态条件的挑战。
附:英文原文
Title: Digital twins for in vivo metabolic flux estimations in patients with brain cancer
Author: Baharan Meghdadi, Wajd N. Al-Holou, Andrew J. Scott, Anjali Mittal, Ningning Liang, Palavalasa Sravya, Abhinav Achreja, Alexandra O’Brien, Kathy Do, Zhe Wu, Jiane Feng, Nathan R. Qi, Vijay Tarnal, Sriram Venneti, C. Ryan Miller, Jann N. Sarkaria, Weihua Zhou, Theodore S. Lawrence, Costas A. Lyssiotis, Daniel R. Wahl, Deepak Nagrath
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-01
Abstract: Recent advancements in metabolic flux estimations in vivo are limited to preclinical models, primarily due to challenges in tissue sampling, tumor microenvironment (TME) heterogeneity, and non-steady-state conditions. To address these limitations and enable flux estimation in human patients, we developed two machine learning-based frameworks. First, the digital twin framework (DTF) integrates first-principles stoichiometric and isotopic simulations with convolutional neural networks to estimate fluxes in patient bulk samples. Second, the single-cell metabolic flux analysis (13C-scMFA) framework combines patient single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data with 13C-isotope tracing, allowing single-cell-level flux quantification. These studies allow quantification of metabolic activity in neoplastic glioma cells, revealing frequently elevated purine synthesis and serine uptake, compared with non-malignant cells. Our models also identify metabolic heterogeneity among patients and mice with brain cancer, in turn predicting treatment responses to metabolic inhibitors. Our frameworks advance in vivo metabolic flux analysis, may lead to novel metabolic therapies, and identify biomarkers for metabolism-directed therapies in patients.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2025.10.022
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(25)00482-6
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
